Combination of circulating miR-145-5p/miR-191-5p as biomarker for breast cancer detection
- PMID: 33362968
- PMCID: PMC7749656
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.10494
Combination of circulating miR-145-5p/miR-191-5p as biomarker for breast cancer detection
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer (BC) is the most common cancer among women worldwide. At present, there is a need to search for new, accurate, reliable, minimally invasive and cheap biomarkers in addition to existing methods for the diagnosis and prognosis of BC. The main goal of this study was to test the diagnostic value of six circulating miRNAs in Kazakh women.
Materials and methods: TaqMan-based miRNA profiling was conducted using plasma specimens from 35 BC women patients and 33 healthy women samples (control group).
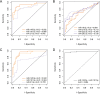
Results: The level of all seven miRNAs (including endogenous control) normalized by synthetic cel-miR-39 were significantly elevated in the group of BC patients. Normalization using miR-222-3p as endogenous control reduced differences in level of miRNAs between groups; as a result, only three miRNAs were significantly upregulated in the group of BC patients-miR-145-5p (P = 6.5e-12), miR-191-5p (P = 3.7e-10) and miR-21-5p (P = 0.0034). Moreover, ROC analysis showed that the use of miR-145-5p and miR-191-5p, both individually (AUC = 0.931 and 0.904, respectively) or in combination (AUC = 0.984), allows to accurately differentiate BC patients from healthy individuals.
Conclusions: Two plasma miRNAs-miR-145-5p and miR-191-5p-are potential biomarkers for diagnosis of BC in the Kazakh population. The findings need to be further substantiated using a more representative sample.
Keywords: Biomarker; Breast cancer; Circulating miRNA; Diagnosis; Kazakh population; Plasma; miR-145; miR-191; miR-21.
©2020 Ashirbekov et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Circulating miRNAs in Untreated Breast Cancer: An Exploratory Multimodality Morpho-Functional Study.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Jun 22;11(6):876. doi: 10.3390/cancers11060876. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31234535 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating microRNAs from the miR-106a-363 cluster on chromosome X as novel diagnostic biomarkers for breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2018 Jul;170(2):257-270. doi: 10.1007/s10549-018-4757-3. Epub 2018 Mar 20. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2018. PMID: 29557526 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a three-miRNA panel in serum for bladder cancer diagnosis by a diagnostic test.Transl Cancer Res. 2022 May;11(5):1005-1016. doi: 10.21037/tcr-21-2611. Transl Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35706801 Free PMC article.
-
The role of miRNAs as biomarkers in breast cancer.Front Oncol. 2024 May 15;14:1374821. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1374821. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38812786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of the Clinical Value of miRNAs and Conventional Biomarkers in AMI: A Systematic Review.Front Genet. 2021 Jun 17;12:668324. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.668324. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34220945 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive Analysis of Correlations in the Expression of miRNA Genes and Immune Checkpoint Genes in Bladder Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 4;22(5):2553. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052553. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33806327 Free PMC article.
-
Panels of circulating microRNAs as potential diagnostic biomarkers for breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2022 Nov;196(1):1-15. doi: 10.1007/s10549-022-06728-8. Epub 2022 Sep 9. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2022. PMID: 36085533
-
A Deep Differential Analysis in Four Subtypes of Breast Cancer Based on Regulations of miRNA-mRNA.IET Syst Biol. 2025 Jan-Dec;19(1):e70020. doi: 10.1049/syb2.70020. IET Syst Biol. 2025. PMID: 40498676 Free PMC article.
-
MiRNA-145-5p Restrains Malignant Behaviors of Breast Cancer Cells Via Downregulating H2AFX Expression.Iran J Biotechnol. 2023 Jul 1;21(3):e3433. doi: 10.30498/ijb.2023.349450.3433. eCollection 2023 Jul. Iran J Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 38344699 Free PMC article.
-
Potential utility of miRNAs for liquid biopsy in breast cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 4;12:940314. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.940314. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35992785 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Andersen CL, Jensen JL, Orntoft TF. Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR data: a model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data sets. Cancer Research. 2004;64(15):5245–5250. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-0496. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

