How Can Alternative Exercise Traditions Help Against the Background of the COVID-19 in Cancer Care? An Overview of Systematic Reviews
- PMID: 33363409
- PMCID: PMC7753005
- DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S282491
How Can Alternative Exercise Traditions Help Against the Background of the COVID-19 in Cancer Care? An Overview of Systematic Reviews
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the quality of systematic reviews/meta-analyses (SR/MAs) on alternative exercise traditions in cancer care.
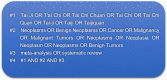
Methods: PubMed, Cochrane Library, Web of Science, Ovid, EBSCOhost, WanFang Database, China National Knowledge Infrastructure, and VIP Database were searched from their inception to June 30, 2020. The search used a combination of subject words and free words. The search terms included "Tai Chi," "Qigong," "Baduanjin," "Yoga," "Pilates," "Cancer," "Meta-analysis," and "Systematic review." Two researchers independently performed literature screening and data extraction and used AMSTAR scale and PRISMA statement to evaluate the methodology and the quality of the evidence.
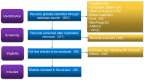
Results: A total of 26 SR/MAs were included. The AMSTAR scale score was 5-10 points, with an average of 7.46±1.33 points. Overall, the methodological quality was considered to be moderate. The PRISMA list score was 13-24 points, with an average of 19.19±2.86 points. Among the papers evaluated, eight reports were relatively complete. A total of 15 papers indicated certain defects. A total of three papers showed relatively serious information defects.
Conclusion: Relative to the control group, alternative exercise traditions may be effective in improving the quality of life, anxiety, depression, distress, and fatigue of cancer patients. However, they may not necessarily improve patients' sleep outcome, body mass index, and pain. During convalescence, cancer patients can be encouraged to start engaging in physical exercise, and professionals can develop appropriate exercise alternatives to ensure the expected effect of exercise while ensuring the safety of patients. The methodological quality of the systematic evaluations of the intervention effects of alternative exercise traditions on cancer patients is not satisfactory. Hence, focus should be directed to the improvement of the preliminary design scheme, publication status, literature retrieval, conflict of interest, and other aspects.
Keywords: COVID-19; alternative exercise traditions; cancer care; overview.
© 2020 Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Global Burden of Disease Cancer Collaboration. Global, regional, and national cancer incidence, mortality, years of life lost, years lived with disability, and disability-adjusted life-years for 32 Cancer Groups, 1990 to 2015 a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study. JAMA Oncol. 2017;3(4):524–548. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2016.5688.. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

