Affinities of the fern genus Ptisana (Marattiaceae) in the Solomon Islands, with descriptions of two new species
- PMID: 33363432
- PMCID: PMC7746669
- DOI: 10.3897/phytokeys.170.59471
Affinities of the fern genus Ptisana (Marattiaceae) in the Solomon Islands, with descriptions of two new species
Abstract
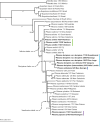
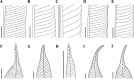
In the process of undertaking a comprehensive review of the pteridophytes of the Solomon Islands, multiple unidentified specimens of the fern genus Ptisana Murdock (Marattiaceae) were collected. Morphological and molecular phylogenetic analyses as well as field observations were required to identify the Solomon Islands taxa. Four species and one variety are recognized from the Solomon Islands: Ptisana ambulans Murdock & C.W. Chen, sp. nov., Ptisana decipiens Murdock & C.W. Chen, sp. nov., Ptisana decipiens var. delicata Murdock & C.W. Chen, var. nov., Ptisana papuana (Alderw.) Murdock & C.W. Chen, comb. nov., and Ptisana smithii (Mett. ex Kuhn) Murdock. The complexities in the identification of Solomon Islands collections show the limits of morphology in the genus and illuminate a path forward for untangling the Ptisana taxonomy on a broader scale.
Keywords: Marattiaceae; Ptisana; Ferns; Solomon Islands; pteridophytes; taxonomy.
Andrew G. Murdock, Cheng-Wei Chen, Yao-Moan Huang, David Glenny.
Figures




References
-
- Brownlie G. (1977) The pteridophyte flora of Fiji. Cramer, Liechtenstein.
-
- Chen C-W, Perrie L, Glenny D, Chiou W-L. (2017) Sol: Amazing Lycophytes & Ferns of the Solomon Islands. National Museum of Natural Science, 550 pp.
-
- Christenhusz MJM, Zhang XC, Schneider H. (2011) A linear sequence of extant families and genera of lycophytes and ferns. Phytotaxa 19(1): 7–54. 10.11646/phytotaxa.19.1.2 - DOI
-
- Christenhusz MJM, Fay MF, Byng JW. (2018) Plant Gateway’s the Global Flora: A practical flora to vascular plant species of the world. Bradford, UK.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
