The Role of the CXCL12/CXCR4/CXCR7 Chemokine Axis in Cancer
- PMID: 33363463
- PMCID: PMC7753359
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.574667
The Role of the CXCL12/CXCR4/CXCR7 Chemokine Axis in Cancer
Abstract
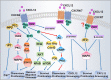
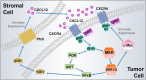
Chemokines are a family of small, secreted cytokines which regulate a variety of cell functions. The C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 12 (CXCL12) binds to C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 (CXCR4) and C-X-C chemokine receptor type 7 (CXCR7). The interaction of CXCL12 and its receptors subsequently induces downstream signaling pathways with broad effects on chemotaxis, cell proliferation, migration, and gene expression. Accumulating evidence suggests that the CXCL12/CXCR4/CXCR7 axis plays a pivotal role in tumor development, survival, angiogenesis, metastasis, and tumor microenvironment. In addition, this chemokine axis promotes chemoresistance in cancer therapy via complex crosstalk with other pathways. Multiple small molecules targeting CXCR4/CXCR7 have been developed and used for preclinical and clinical cancer treatment. In this review, we describe the roles of the CXCL12/CXCR4/CXCR7 axis in cancer progression and summarize strategies to develop novel targeted cancer therapies.
Keywords: C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4; C-X-C chemokine receptor type 7; C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 12; cancer progression; tumor microenvironment.
Copyright © 2020 Shi, Riese and Shen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bagri A., Gurney T., He X., Zou Y. R., Littman D. R., Tessier-Lavigne M., et al. (2002). The chemokine SDF1 regulates migration of dentate granule cells. Development 129, 4249–4260. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

