Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Geniposide on Regulating the Functions of Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Fibroblasts via Inhibiting Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Receptors1/3 Coupling Gαi/Gαs Conversion
- PMID: 33363467
- PMCID: PMC7753157
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.584176
Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Geniposide on Regulating the Functions of Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Fibroblasts via Inhibiting Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Receptors1/3 Coupling Gαi/Gαs Conversion
Abstract
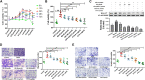
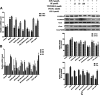
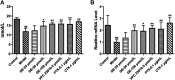
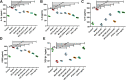
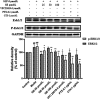
The activated Gα protein subunit (Gαs) and the inhibitory Gα protein subunit (Gαi) are involved in the signal transduction of G protein coupled receptors (GPCRs). Moreover, the conversion of Gαi/Gαs can couple with sphingosine-1-phosphate receptors (S1PRs) and have a critical role in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Through binding to S1PRs, sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) leads to activation of the pro-inflammatory signaling in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts (RASFs). Geniposide (GE) can alleviate RASFs dysfunctions to against RA. However, its underlying mechanism of action in RA has not been elucidated so far. This study aimed to investigate whether GE could regulate the biological functions of MH7A cells by inhibiting S1PR1/3 coupling Gαi/Gαs conversion. We use RASFs cell line, namely MH7A cells, which were obtained from the patient with RA and considered to be the main effector cells in RA. The cells were stimulated with S1P (5 μmol/L) and then were treated with or without different inhibitors: Gαi inhibitor pertussis toxin (0.1 μg/mL), S1PR1/3 inhibitor VPC 23019 (5 μmol/L), Gαs activator cholera toxin (1 μg/mL) and GE (25, 50, and 100 μmol/L) for 24 h. The results showed that GE may inhibit the abnormal proliferation, migration and invasion by inhibiting the S1P-S1PR1/3 signaling pathway and activating Gαs or inhibiting Gαi protein in MH7A cells. Additionally, GE could inhibit the release of inflammatory factors and suppress the expression of cAMP, which is the key factor of the conversion of Gαi and Gαs. GE could also restore the dynamic balance of Gαi and Gαs by suppressing S1PR1/3 and inhibiting Gαi/Gαs conversion, in a manner, we demonstrated that GE inhibited the activation of Gα downstream ERK protein as well. Taken together, our results indicated that down-regulation of S1PR1/3-Gαi/Gαs conversion may play a critical role in the effects of GE on RA and GE could be an effective therapeutic agent for RA.
Keywords: fibroblast-like synoviocytes; geniposide; gαi-gαs conversion; rheumatoid arthritis; sphingosine-1-phosphate; sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1/3.
Copyright © 2020 Wang, Dai, Wu, Wang, Deng, Wang, Bu, Sun and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Afzali M. F., Popichak K. A., Burton L. H., Klochak A. L., Wilson W. J., Safe S., et al. (2018). A novel diindolylmethane analog, 1,1-bis(3'-indolyl)-1-(p-chlorophenyl) methane, inhibits the tumor necrosis factor-induced inflammatory response in primary murine synovial fibroblasts through a Nurr1-dependent mechanism. Mol. Immunol. 101, 46–54. 10.1016/j.molimm.2018.05.024 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bourgoin S. G., Zhao C., Fernandes M. J. (2012). “Targeting the Metabolism and Receptors of Sphingosine‐1‐ Phosphate for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis,” in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Editor A. Lemmey (London, FL: InTech). Editor A. Lemmey (London, FL: InTech), 196–210.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

