Umbilical cord lactate compared with pH as predictors of intrapartum asphyxia
- PMID: 33363591
- PMCID: PMC7725025
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2020.9513
Umbilical cord lactate compared with pH as predictors of intrapartum asphyxia
Abstract
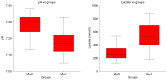
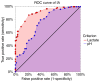
Despite advances in fetal monitoring during labor, one of the most critical causes of neonatal death and neurologic injuries remains intrapartum asphyxia. Umbilical cord gases can be used to detect acidosis and fetal distress. We conducted a retrospective, multicenter study to evaluate umbilical cord blood pH and lactate as a mean of evaluating the degree of intrapartum hypoxia and also to establish which of the two is more reliable in predicting morbidity in term neonates. The present study utilized a total of 124 cases that met the criteria for intrapartum asphyxia and 150 normal term newborns that were randomly selected as case control. Both umbilical cord lactate and pH proved to be accurate predictors of neonatal morbidity caused by intrapartum hypoxia. Lactate proved to be superior to pH in predicting adverse neonatal outcome. The greatest sensibility and specificity in predicting intrapartum asphyxia were achieved in our study by using a cutoff value of 3.75 mmol/l for lactate and 7.24 for pH.
Keywords: fetal distress; intrapartum asphyxia; intrapartum hypoxia; umbilical cord lactate; umbilical cord pH.
Copyright © 2020, Spandidos Publications.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Proposed cutoff for fetal scalp blood lactate in intrapartum fetal surveillance based on neonatal outcomes: a large prospective observational study.BJOG. 2022 Mar;129(4):636-646. doi: 10.1111/1471-0528.16924. Epub 2021 Oct 4. BJOG. 2022. PMID: 34555249
-
Intrapartum fetal asphyxia: study of umbilical cord blood lactate in relation to fetal heart rate patterns.Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2013 Jun;287(6):1067-73. doi: 10.1007/s00404-012-2694-7. Epub 2012 Dec 29. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2013. PMID: 23274793
-
Prevention of cerebral palsy during labour: role of foetal lactate.Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2008 Jul;278(1):17-22. doi: 10.1007/s00404-007-0531-1. Epub 2007 Dec 11. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2008. PMID: 18071726
-
[Rapid microanalysis of lactate in cord blood and at fetal scalp blood sampling].Gynecol Obstet Fertil. 2004 Mar;32(3):241-4. doi: 10.1016/j.gyobfe.2004.01.010. Gynecol Obstet Fertil. 2004. PMID: 15123123 Review. French.
-
A Global View of Neonatal Asphyxia and Resuscitation.Front Pediatr. 2019 Nov 26;7:489. doi: 10.3389/fped.2019.00489. eCollection 2019. Front Pediatr. 2019. PMID: 31850287 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Maternal and umbilical cord blood lactate for predicting perinatal death: a secondary analysis of data from a randomized controlled trial.BMC Pediatr. 2023 Apr 18;23(1):179. doi: 10.1186/s12887-023-04008-y. BMC Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37072754 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Lactate, an Essential Metabolic Marker in the Diagnosis and Management of Pediatric Conditions.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Mar 23;15(7):816. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15070816. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40218166 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The association of umbilical hyperlactatemia with short- and tong-term outcomes in extremely low birth weight neonates: a matched cohort study.Eur J Pediatr. 2025 May 7;184(6):328. doi: 10.1007/s00431-025-06147-z. Eur J Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40332591 Free PMC article.
-
Association between Serum Lactate and Morbidity and Mortality in Neonates: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Children (Basel). 2023 Nov 8;10(11):1796. doi: 10.3390/children10111796. Children (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38002887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fetal Wellbeing Monitoring: A Review Article.Cureus. 2022 Sep 11;14(9):e29039. doi: 10.7759/cureus.29039. eCollection 2022 Sep. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36249607 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Freeman JM, Nelson KB. Intrapartum asphyxia and cerebral palsy. Pediatrics. 1988;82:240–249. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous