A NOVEL INTRAGENIC DELETION RELATED TO THE ARGININE VASOPRESSIN V2 RECEPTOR CAUSES NEPHROGENIC DIABETES INSIPIDUS
- PMID: 33363649
- PMCID: PMC7748242
- DOI: 10.4183/aeb.2020.295
A NOVEL INTRAGENIC DELETION RELATED TO THE ARGININE VASOPRESSIN V2 RECEPTOR CAUSES NEPHROGENIC DIABETES INSIPIDUS
Abstract
Background: Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (NDI) is a disease characterized by a defective response to the antidiuretic hormone (ADH) of the renal collecting duct leading to a decline in the ability of the pro-urine concentration.
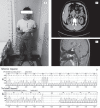
Case presentation: A 23-year-old man presented with an over 20-year history of polyuria concomitant with hydronephrosis. The diagnosis of NDI was established by gene analysis as well as a water-deprivation and vasopressin test. All exons of arginine vasopressin V2 receptor (AVPR2) gene were amplified and sequenced. A novel hemizygous intragenic inframe deletion, cDNA 255th bp to 263th bp in exon 2 of AVPR2, was identified. These relevant translations from the 85th amino acid Asp to 88th amino acid Val were missed and replaced by amino acid Glu. After treating the patient with hydrochlorothiazide, his symptoms improved significantly.
Conclusion: The genetic analysis revealed a novel X-linked intragenic inframe deletion, AVPR2 gene cDNA 255th bp to 263th bp, causing NDI.
Keywords: Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus; arginine vasopressin V2 receptor; intragenic inframe deletion; polyuria.
©by Acta Endocrinologica Foundation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Di Iorgi N, Napoli F, Allegri AE, Olivieri I, Bertelli E, Gallizia A, Rossi A, Maghnie M. Diabetes insipidus - diagnosis and management. Horm Res Paediatr. 2012;77(2):69–84. - PubMed
-
- Kavanagh C, Uy NS. Nephrogenic Diabetes Insipidus. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2019;66(1):227–234. - PubMed
-
- Sasaki S, Chiga M, Kikuchi E, Rai T, Uchida S. Hereditary nephrogenic diabetes insipidus in Japanese patients: analysis of 78 families and report of 22 new mutation deletions in AVPR2 and AQP2. Clinical & Experimental Nephrology. 2013;17(3):338–344. - PubMed
-
- Juul KV, Bichet DG, Nielsen S, Nørgaard JP. The physiological and pathophysiological functions of renal and extrarenal vasopressin V2 receptors. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2014;306(9):931–940. - PubMed
-
- Bichet DG, Bockenhauer D. Genetic forms of nephrogenic diabetes insipidus (NDI): Vasopressin receptor defect (X-linked) and aquaporin defect (autosomal recessive and dominant) Best Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 2016;30(2):263–276. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
