Brain abscess and periodontal pathogens (Fusobacterium Nucleatum). Report of a case
- PMID: 33363764
- PMCID: PMC7752455
- DOI: 10.1002/ccr3.3173
Brain abscess and periodontal pathogens (Fusobacterium Nucleatum). Report of a case
Abstract
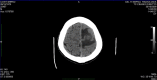
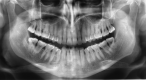
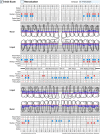
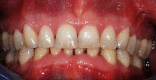
Patients who develop brain abscesses must be evaluated through a complete set of diagnostic tests including a microbiological and clinical periodontal assessment. A genetic comparison of the pathogens from intracranial/extracranial sites is necessary.
Keywords: Fusobacterium Nucleatum; brain abscess; periodontal pathogens.
© 2020 The Authors. Clinical Case Reports published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Moazzam AA, Rajagopal SM, Sedghizadeh PP, Zada G, Habibian M. Intracranial bacterial infections of oral origin. J Clin Neurosci. 2015;22:800‐806. - PubMed
-
- Lazow SK, Izzo SR, Vasquez D. Do dental infections really cause central nervous system infections? Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 2011;23:569‐578. - PubMed
-
- Bolger AF. The rationale for the new infective endocarditis guidelines. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2009;11:101‐108. - PubMed
-
- Carmona IT, Diz Dios P, Scully C. An update on the controversies in bacterial endocarditis of oral origin. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2002;93:660‐670. - PubMed
-
- Gendron R, Grenier D, Maheu‐Robert L. The oral cavity as a reservoir of bacterial pathogens for focal infections. Microbes Infect. 2000;2:897‐906. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

