Extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma in an 11-year-old child
- PMID: 33364024
- PMCID: PMC7752305
- DOI: 10.1002/ccr3.3474
Extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma in an 11-year-old child
Abstract
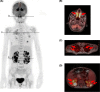
Extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma (ENKTL) is difficult to identify and diagnose appropriately. Positron emission tomography imaging is a crucial method that leads to precise diagnosis. A proper regimen including stem cell transplantation would possibly improve prognosis of advanced ENKTL.
Keywords: SMILE therapy; extranodal natural killer/T‐cell lymphoma; hemophagocytic syndrome.
© 2020 The Authors. Clinical Case Reports published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Kandai Nozu has received consulting fees from Kyowa Kirin Co., Ltd.; and lecture fees from Kyowa Kirin Co., Ltd., Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation, and Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Kazumoto Iijima has received grant support from Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd.; consulting fees from Kyowa Kirin Co., Ltd., and Boehringer Ingelheim; and lecture fees from Kyowa Kirin Co., Ltd., Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Takeda Pharmaceutical Company, Integrated Development Associates, and Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation. The other authors declare that no conflicts of interest exist.
Figures
References
-
- Henter JI, Horne A, Arico M, et al. HLH‐2004: Diagnostic and therapeutic guidelines for hemophagocytic lymphohistocytosis. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2007;48(2):124‐131. - PubMed
-
- Yamaguchi M, Kwong YL, Kim WS, et al. Phase II study of SMILE chemotherapy for newly diagnosed stage IV, relapsed, or refractory extranodal natural killer (NK)/T‐cell lymphoma, nasal type: the NK‐Cell Tumor Study Group study. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(33):4410‐4416. - PubMed
-
- Kim SJ, Park S, Kang ES, et al. Induction treatment with SMILE and consolidation with autologous stem cell transplantation for newly diagnosed stage IV extranodal natural killer/T‐cell lymphoma patients. Ann Hematol. 2015;94(1):71‐78. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources