Cardiopulmonary arrest secondary to compression of the heart owing to esophageal hiatal hernia: a case report
- PMID: 33364036
- PMCID: PMC7750025
- DOI: 10.1002/ams2.615
Cardiopulmonary arrest secondary to compression of the heart owing to esophageal hiatal hernia: a case report
Abstract
Background: Esophageal hiatal hernia is commonly encountered in clinical practice. We describe a case of cardiac compression caused by an esophageal hiatal hernia that resulted in circulatory failure and cardiac arrest.
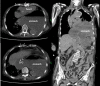
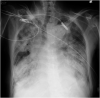
Case presentation: An 82-year-old woman presented to our hospital with vomiting, which progressed to cardiac arrest in the emergency room after computed tomography (CT) imaging. CT revealed gastric herniation into the mediastinum, with marked cardiac compression. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation was performed, and a nasogastric tube was inserted for gastric decompression, which resulted in the return of spontaneous circulation and subsequent hemodynamic stabilization. However, the patient died of aspiration pneumonia 4 days later.
Conclusion: Gastric decompression can lead to rapid improvements in respiration and circulation in patients with an esophageal hiatal hernia. Nonetheless, to prevent complications, such as those observed in our patient, definitive surgical treatment is warranted.
Keywords: Circulatory failure; diaphragmatic hernia; esophageal hiatal hernia; tension gastrothorax; upside‐down stomach.
© 2020 The Authors. Acute Medicine & Surgery published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Association for Acute Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Approval of the research protocol: N/A. Informed Consent: As the patient is dead, we have carefully deidentified the patient’s information. The patient’s family has consented to the submission of the case report for publication in the journal. We have not involved the Ethics Committee because we did not carry out invasive treatment or tests for research purposes. Registry and the Registration No. of the study/Trial: N/A. Animal Studies: N/A. Conflict of Interest: None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Yu HX, Han CS, Xue JR, Han Z‐F, Xin H. Esophageal hiatal hernia: risk, diagnosis, and management. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018; 12: 319–29. - PubMed
-
- Siegal SR, Dolan JP, Hunter JG. Modern diagnosis and treatment of hiatal hernias. Langenbecks Arch. Surg. 2017; 402: 1145–51. - PubMed
-
- Allen MS, Trastek VF, Deschamps C, Pairolero PC. Intrathoracic stomach. Presentation and results of operation. J. Thorac Cardiovasc. Surg. 1993; 105: 253–8. - PubMed
-
- Wirsching A, Klevebro F, Boshier PR et al The other explanation for dyspnea: giant paraesophageal hiatal hernia repair routinely improves pulmonary function. Di.s Esophagus. 2019; 32: doz032. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

