Mind Health Before and After Total Knee Arthroplasty
- PMID: 33364660
- PMCID: PMC7748925
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0040-1708519
Mind Health Before and After Total Knee Arthroplasty
Abstract
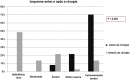
Objective To assess the preoperative and postoperative outcomes of patients diagnosed with severe knee osteoarthritis who underwent a total knee arthroplasty (TKA) using a mobile-bearing implant with a rotating platform and removing the posterior cruciate ligament. The present study focused on the outcomes relative to depression, pain, functional limitations, and fall episodes. Methods The Lequesne questionnaire was used to assess pain and functional limitations before and after TKA. In addition, the geriatric depression scale (GDS) was also used. Episodes of falls before and after the surgery were estimated. Results The mean Lequesne score before the surgery was 15.95, and that after surgery was 6.5. This finding was statistically significant ( p < 0.001). The mean GDS score before the surgery was 7.43, and that after TKA was 2.22 ( p < 0.001). The mean number of fall occurrences before the procedure, over a 1-year period, was 1.22, and that after TKA was 0.27 ( p = 0.004). A direct relationship was found between the Lequesne scores before the surgery and the GDS scores ( p = 0.004). Conclusions Total knee arthroplasty resulted in the improvement of pain and functional limitation, decrease or disappearance of the depressive condition, and decrease of fall rates in the evaluated patients.
Keywords: arthroplasty, replacement, knee; depression; osteoarthritis.
Sociedade Brasileira de Ortopedia e Traumatologia. This is an open access article published by Thieme under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonDerivative-NonCommercial License, permitting copying and reproduction so long as the original work is given appropriate credit. Contents may not be used for commercial purposes, or adapted, remixed, transformed or built upon. ( https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ ).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflito de Interesses Os autores declaram não haver conflito de interesses.
Figures
References
-
- Piano L P, Golmia R P, Scheinberg M.Artroplastia total de quadril e joelho: aspectos clínicos na fase perioperatória Einstein (Sao Paulo) 20108(3 Pt 1):350–353. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources