Gallic Acid Alleviates Gouty Arthritis by Inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and Pyroptosis Through Enhancing Nrf2 Signaling
- PMID: 33365024
- PMCID: PMC7750458
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.580593
Gallic Acid Alleviates Gouty Arthritis by Inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and Pyroptosis Through Enhancing Nrf2 Signaling
Abstract
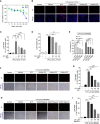
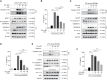
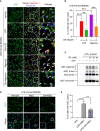
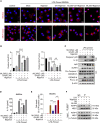
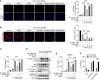
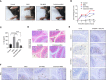
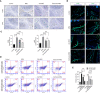
Gallic acid is an active phenolic acid widely distributed in plants, and there is compelling evidence to prove its anti-inflammatory effects. NLRP3 inflammasome dysregulation is closely linked to many inflammatory diseases. However, how gallic acid affects the NLRP3 inflammasome remains unclear. Therefore, in the present study, we investigated the mechanisms underlying the effects of gallic acid on the NLRP3 inflammasome and pyroptosis, as well as its effect on gouty arthritis in mice. The results showed that gallic acid inhibited lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release and pyroptosis in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-primed and ATP-, nigericin-, or monosodium urate (MSU) crystal-stimulated macrophages. Additionally, gallic acid blocked NLRP3 inflammasome activation and inhibited the subsequent activation of caspase-1 and secretion of IL-1β. Gallic acid exerted its inhibitory effect by blocking NLRP3-NEK7 interaction and ASC oligomerization, thereby limiting inflammasome assembly. Moreover, gallic acid promoted the expression of nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and reduced the production of mitochondrial ROS (mtROS). Importantly, the inhibitory effect of gallic acid could be reversed by treatment with the Nrf2 inhibitor ML385. NRF2 siRNA also abolished the inhibitory effect of gallic acid on IL-1β secretion. The results further showed that gallic acid could mitigate MSU-induced joint swelling and inhibit IL-1β and caspase 1 (p20) production in mice. Moreover, gallic acid could moderate MSU-induced macrophages and neutrophils migration into joint synovitis. In summary, we found that gallic acid suppresses ROS generation, thereby limiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation and pyroptosis dependent on Nrf2 signaling, suggesting that gallic acid possesses therapeutic potential for the treatment of gouty arthritis.
Keywords: NLRP3 inflammasome; Nrf2; gallic acid; gouty arthritis; pyroptosis.
Copyright © 2020 Lin, Luo, Weng, Huang, Yao, Fu, Li, Liu, Li, Chen and Pan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Geraniin restricts inflammasome activation and macrophage pyroptosis by preventing the interaction between ASC and NLRP3 to exert anti-inflammatory effects.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Mar 10;129:111656. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.111656. Epub 2024 Feb 9. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38340422
-
Corilagin Restrains NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation and Pyroptosis through the ROS/TXNIP/NLRP3 Pathway to Prevent Inflammation.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Oct 17;2022:1652244. doi: 10.1155/2022/1652244. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 36299604 Free PMC article.
-
Anemoside B4 targets NEK7 to inhibit NLRP3 inflammasome activation and alleviate MSU-induced acute gouty arthritis by modulating the NF-κB signaling pathway.Phytomedicine. 2025 Mar;138:156407. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2025.156407. Epub 2025 Jan 17. Phytomedicine. 2025. PMID: 39939033
-
ALK-JNK signaling promotes NLRP3 inflammasome activation and pyroptosis via NEK7 during Streptococcus pneumoniae infection.Mol Immunol. 2023 May;157:78-90. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2023.03.016. Epub 2023 Mar 29. Mol Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37001294 Review.
-
Recent advances in the NEK7-licensed NLRP3 inflammasome activation: Mechanisms, role in diseases and related inhibitors.J Autoimmun. 2020 Sep;113:102515. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2020.102515. Epub 2020 Jul 20. J Autoimmun. 2020. PMID: 32703754 Review.
Cited by
-
Virtual screening combined with experimental verification reveals the potential mechanism of Fuzitang decoction against Gouty Arthritis.Heliyon. 2023 Nov 25;9(12):e22650. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e22650. eCollection 2023 Dec. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38058447 Free PMC article.
-
Nrf2 Inhibits the Progression of Parkinson's Disease by Upregulating AABR07032261.5 to Repress Pyroptosis.J Inflamm Res. 2022 Feb 2;15:669-685. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S345895. eCollection 2022. J Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 35140498 Free PMC article.
-
Gallic Acid Alleviates Visceral Pain and Depression via Inhibition of P2X7 Receptor.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 31;23(11):6159. doi: 10.3390/ijms23116159. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35682841 Free PMC article.
-
Causal association between tea intake and risk for gout: a Mendelian randomization study.Front Genet. 2023 Jul 13;14:1220931. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1220931. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37519890 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the potential immunomodulatory effects of gallic acid on milk phagocytes in bovine mastitis caused by Staphylococcus aureus.Front Vet Sci. 2023 Sep 15;10:1255058. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1255058. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 37781277 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Subramanian AP, John AA, Vellayappan MV, Balaji A, Jaganathan SK, Supriyanto E, et al. Gallic acid: prospects and molecular mechanisms of its anticancer activity. Rsc Adv (2015) 5:35608–21. 10.1039/c5ra02727f - DOI
-
- Hsiang CY, Hseu YC, Chang YC, Kumar KJ, Ho TY, Yang HL. Toona sinensis and its major bioactive compound gallic acid inhibit LPS-induced inflammation in nuclear factor-kappaB transgenic mice as evaluated by in vivo bioluminescence imaging. Food Chem (2013) 136:426–34. 10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.08.009 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

