Safety of apatinib plus S-1 for advanced solid tumor as palliative treatment
- PMID: 33365062
- PMCID: PMC7716638
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2020.9494
Safety of apatinib plus S-1 for advanced solid tumor as palliative treatment
Abstract
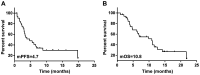
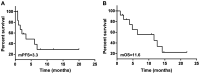
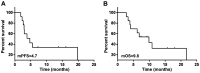
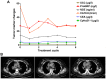
The aim of the present study was to explore the safety of apatinib plus S-1 in treating advanced solid tumors after failure of two or more lines of chemotherapy. A total of 33 patients with advanced cancer treated between April 2016 to March 2019 were retrospectively analyzed. Of these, 13 patients had non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), 13 patients had SCLC, 4 patients had esophageal cancer and 3 had cervical cancer. All patients were treated with apatinib 250 mg once daily combined with S-1 60 mg/m2 twice daily for 14 days, repeated every 3 weeks. Adverse reactions were observed until aggravation of adverse reactions beyond the tolerable range or disease progression, and the survival rate and clinical benefits were calculated. The results suggested that the incidence rate of adverse effects (grade 3-4) was 45.5% (15/33). The top three severe adverse effects were hypertension (15.2%), thrombocytopenia (12.1%) and proteinuria (9.1%). A total of 2 patients with lung squamous-cell carcinomas died of severe pulmonary hemorrhage. Other adverse reactions were tolerated in the cohort. A total of 10 patients achieved partial response and the objective response rate was 30.3%. Furthermore, 13 patients achieved stable disease and 10 patients had progressive disease, and accordingly, the disease control rate was 72.7%. In conclusion, apatinib plus S-1 for advanced solid tumor patients as palliative treatment have a certain efficacy and was relatively safe but should be used with caution in patients with squamous-cell lung carcinoma and the efficacy and safety requires further assessment.
Keywords: advanced solid tumor; adverse reactions; apatinib; safety.
Copyright: © Chen et al.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Clinical efficacy and safety of apatinib combined with S-1 in advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Invest New Drugs. 2020 Apr;38(2):500-506. doi: 10.1007/s10637-019-00866-5. Epub 2019 Oct 24. Invest New Drugs. 2020. PMID: 31650447 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of camrelizumab plus apatinib as second-line treatment for advanced squamous non-small cell lung cancer.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Apr;10(8):441. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-4792. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35571422 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and Efficacy of Low-Dosage Apatinib Monotherapy in Advanced Lung Squamous-Cell Carcinoma: A Prospective Cohort Study.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Nov 10;13:11529-11535. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S277532. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 33204107 Free PMC article.
-
Low-dose apatinib monotherapy in advanced chemotherapy-refractory small cell lung cancer: a case series and literature review.J Int Med Res. 2020 Mar;48(3):300060519887276. doi: 10.1177/0300060519887276. Epub 2019 Dec 18. J Int Med Res. 2020. PMID: 31847652 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Successful treatment using apatinib with or without docetaxel in heavily pretreated advanced non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer: A case report and literature review.Cancer Biol Ther. 2018 Mar 4;19(3):141-144. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2017.1414757. Epub 2018 Jan 15. Cancer Biol Ther. 2018. PMID: 29261000 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in monotherapy and combination therapy of S-1 for patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a narrative review.Transl Cancer Res. 2024 Apr 30;13(4):2012-2025. doi: 10.21037/tcr-23-2019. Epub 2024 Apr 9. Transl Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38737682 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- van Hagen P, Hulshof MC, van Lanschot JJ, Steyerberg EW, van Berge Henegouwen MI, Wijnhoven BP, Richel DJ, Nieuwenhuijzen GA, Hospers GA, Bonenkamp JJ, et al. Preoperative chemoradiotherapy for esophageal or junctional cancer. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:2074–2084. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1112088. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
