Injectable progesterone in timed artificial insemination programs in beef cows
- PMID: 33365090
- PMCID: PMC7746219
- DOI: 10.21451/1984-3143-2017-AR928
Injectable progesterone in timed artificial insemination programs in beef cows
Abstract
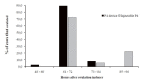
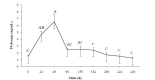
The aims of this study were I) to compare the follicular diameter, corpus luteum diameter and serum progesterone (P4) concentrations in cows treated with conventional protocol vs. injectable P4 protocol; II) to determine the serum P4 profile in ovariectomized heifers; and III) to compare pregnancy rate between protocols. In experiment I, multiparous cows received a protocol for ovulation synchronization with an intravaginal P4 device (n = 38; device + EB day 0; device removal + PGF2α + eCG + EC day 8) or injectable P4 (n = 38; injection + EB day 0; PGF2α + eCG + EC day 8). In experiment II, ovariectomized heifers (n = 8) were treated with injectable P4 and blood samples were collected to determine the serum P4 profile. In experiment III, multiparous cows were timed AI with two different P4 approaches, intravaginal P4 device (n = 48) or injectable P4 (n = 47). In the first experiment, cows treated with P4 device had higher (P < 0.05) diameter of dominant follicle after ovulation induction (11.6 ± 1.8 vs.10.3 ± 1.8 mm) and ovulation rate (97%, 37/38 vs. 47.3%, 18/38) than cows treated with injectable P4. But, the follicular growth daily was higher (P < 0.05) in cows treated with injectable P4 than intravaginal device (1.3 ± 0.4 vs. 1.0 ± 0.3 mm/day, respectively). In experiment II, the P4 concentration peak occurred within 48 hours (6.54 ng/mL) and decreased after 96 hours (P < 0.05) after P4 injection. In experiment III, cows with P4 device had higher (P < 0.05) pregnancy rate than the injectable P4 group (60.4 vs. 34.0%, respectively). These results demonstrate that although the intravaginal P4 devices showed a higher pregnancy rate, a protocol with injectable P4 represents an easier method and a promising alternative for TAI in cattle.
Keywords: follicular diameter; injectable progesterone; pregnancy; synchronization of ovulation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ovulation synchronization with estradiol benzoate or GnRH in a timed artificial insemination protocol in buffalo cows and heifers during the nonbreeding season.Theriogenology. 2017 Jan 1;87:333-338. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2016.09.006. Epub 2016 Sep 13. Theriogenology. 2017. PMID: 27743689 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of circulating progesterone concentration during synchronization for fixed-time artificial insemination on ovulation and fertility in Bos indicus (Nelore) beef cows.Theriogenology. 2015 Apr 1;83(6):1093-100. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2014.12.009. Epub 2014 Dec 12. Theriogenology. 2015. PMID: 25619807 Clinical Trial.
-
Use of injectable progesterone to replace the intravaginal progesterone device on the ovulation synchronization protocol reduces the pregnancy rate in Bos indicus cows.Theriogenology. 2023 Jan 1;195:55-61. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2022.10.008. Epub 2022 Oct 13. Theriogenology. 2023. PMID: 36283227
-
Hormonal strategy to reduce suckled beef cow handling for timed artificial insemination with sex-sorted semen.Theriogenology. 2018 Jul 1;114:159-164. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2018.03.020. Epub 2018 Mar 21. Theriogenology. 2018. PMID: 29626739 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of two intravaginal progesterone releasing devices (PRID-Delta vs CIDR) in dairy cows: blood progesterone profile and field fertility.Anim Reprod Sci. 2013 May;138(3-4):143-9. doi: 10.1016/j.anireprosci.2013.02.010. Epub 2013 Feb 22. Anim Reprod Sci. 2013. PMID: 23523234 Review.
References
-
- Ayres H , Martins CM , Ferreira RM , Mello JE , Dominguez JH , Souza AH , Valentin R , Santos IC , Baruselli PS. Effect of timing of estradiol benzoate administration upon synchronization of ovulation in suckling Nelore cows (Bos indicus) treated with a progesterone-releasing intravaginal device . Anim Reprod Sci. 2008;109:77–87. - PubMed
-
- Barreiros TR , Blaschi W , Santos GM , Morotti F , Andrade ER , Baruselli PS , Seneda MM. Dynamics of follicular growth and progesterone concentrations in cyclic and anestrous suckling Nelore cows (Bos indicus) treated with progesterone, equine chorionic gonadotropin, or temporary calf removal . Theriogenology. 2014;81:651–656. - PubMed
-
- Baruselli PS , Reis EL , Marques MO , Nasser LF , Bó GA. The use of hormonal treatments to improve reproductive performance of anestrous beef cattle in tropical climates . Anim Reprod Sci. 2004;82:479–486. - PubMed
-
- Bo GA , Baruselli PS , Martinez MF. Pattern and manipulation of follicular development in Bos indicus cattle . Anim Reprod Sci. 2003;78:307–326. - PubMed
-
- Campos JT , Marinho LS , Lunardelli PA , Morotti F , Seneda MM. Resynchronization of estrous cycle with eCG and temporary calf removal in lactating Bos indicus cows . Theriogenology. 2013;80:619–623. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
