Effect of aflatoxin B1 on blood serum oestradiol-17β and progesterone concentrations during the luteal phase and the synchronized oestrus of goats
- PMID: 33365099
- PMCID: PMC7746212
- DOI: 10.21451/1984-3143-2017-AR939
Effect of aflatoxin B1 on blood serum oestradiol-17β and progesterone concentrations during the luteal phase and the synchronized oestrus of goats
Abstract
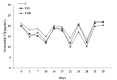
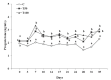
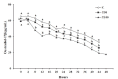
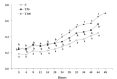
The effect of prolonged aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) administration on blood serum oestradiol-17β and progesterone concentrations in goats during the luteal phase and the synchronized oestrus was investigated. Thirty-six Greek indigenous primiparous goats were used, during the oestrus period; 12 goats received, per os, 50 μg (treated group T50) and 12 goats received 100 μg (treated group T100) AFB1/day/head, respectively, for approximately 1.5 month, while 12 goats served as controls (C). On day 36 of the experiment, each goat was injected, i.m, 0.5 ml prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α). Blood samples were collected from each goat twice a week, before PGF2α injection, as well as every 4 hours from the onset to the end of the synchronized oestrus. Oestradiol-17β and progesterone concentrations in blood serum were determined using radioimmunoassay. During the whole luteal(s) phase(s), linear regression analysis revealed a significant negative dependence (P < 0.05) of oestradiol-17β and a significant positive dependence (P < 0.05) of progesterone over group (C = 0, T50 = 50, T100 = 100), in a dose dependent manner. During the synchronized oestrus, multiple linear regression analysis revealed a significant negative dependence (P < 0.05) of oestradiol-17β, as well as a significant positive dependence (P < 0.05) of progesterone over group (C = 0, T50 = 50, T100 = 100) and over time (hours, from the onset to the end of the synchronized oestrus). No significant differences were noticed among the three groups, regarding the body weight of the goats from the onset to the end of AFB1 administration, the occurrence or the duration of the synchronized oestrus presented by the goats (P > 0.05). In conclusion, prolonged AFB1 administration at doses of 100 or even of 50 μg/day/head changes the hormonal pattern in blood during the luteal phase and the synchronized oestrus of goats, being in oestrus period.
Keywords: AFB1; hormones; mycotoxins; reproduction; ruminants.
Figures
References
-
- Abdulrazzaq YM , Osman N , Yousif ZM , Al-Falahi S. Aflatoxin M1 in breast-milk of U.A.E. women. Ann Trop Paediatr. 2003;23:173–179. - PubMed
-
- Akiyama H , Goda Y , Tanaka T , Toyoda M. Determination of aflatoxins B1, B2, G1 and G2 in spices using a multifunctional column clean-up . J Chromatogr A. 2001;932:153–157. - PubMed
-
- Bastaki SA , Osman N , Kochiyil J , Shafiullah M , Padmanabhan R , Abdulrazzaq YM. Toxicokinetics of aflatoxin in pregnant mice. Int J Toxicol. 2010;29:425–431. - PubMed
-
- Battacone G , Nudda A , Cannas A , Cappio Borlino A , Bomboi G , Pulina G. Excretion of aflatoxin M1 in milk of dairy ewes treated with different doses of aflatoxin B1 . J Dairy Sci. 2003;86:2667–2675. - PubMed
-
- Bauernfeind M , Holtz W. Progesterone and estrogen levels in serum of cyclic goats measured by enzyme immunoassay . Small Rum Res. 1991;6:95–102.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
