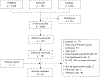
Feasible but Not Yet Efficacious: A Scoping Review of Wearable Activity Monitors in Interventions Targeting Physical Activity, Sedentary Behavior, and Sleep
- PMID: 33365227
- PMCID: PMC7751894
- DOI: 10.1007/s40471-020-00229-2
Feasible but Not Yet Efficacious: A Scoping Review of Wearable Activity Monitors in Interventions Targeting Physical Activity, Sedentary Behavior, and Sleep
Abstract
Purpose of review: The present review aimed to explore the range and characteristics of interventions that utilize WAM and descriptively summarize the efficacy of these interventions.
Recent findings: A total of 65 articles (61 studies) were included in this review. Most of the WAM-based interventions (n=58) were designed to improve physical activity (PA). Interventions targeting sedentary behavior (SB) were much less common (n=12), and even less frequent were WAM-based sleep interventions (n=3). Most studies tested the feasibility of WAM-based interventions; hence, efficacy of these interventions in improving PA, SB, and/or sleep could not be conclusively determined. Nonetheless, WAM-based interventions showed considerable potential in increasing PA and decreasing SB.
Summary: WAM-based PA interventions exhibited preliminary efficacy in increasing PA. Although not as many interventions were focused on SB, current interventions also showed potential in decreasing sedentary time. Meanwhile, more evidence is needed to determine the utility of WAM in improving sleep. Major challenges with including WAM as part of interventions are reduced engagement in using the devices over time and the rapid changes in technology resulting in devices becoming obsolete soon after completion of an efficacy trial.
Keywords: fitness trackers; physical activity; sedentary behavior; sleep; wearable activity monitors.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: Dr. Kline reports grants from National Institutes of Health outside of the submitted work. The other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- International Data Corportation, Wrist-worn wearables maintain a strong growth trajectory in Q2 2019, according to IDC. 2019, Press release from IDC on September 12, 2019..
-
- Straiton N, et al., The validity and reliability of consumer-grade activity trackers in older, community-dwelling adults: A systematic review. Maturitas, 2018. 112: p. 85–93. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials