The complete chloroplast genome of Hibiscus Taiwanensis (Malvaceae)
- PMID: 33365613
- PMCID: PMC7687590
- DOI: 10.1080/23802359.2019.1640084
The complete chloroplast genome of Hibiscus Taiwanensis (Malvaceae)
Abstract
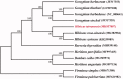
Hibiscus taiwanensis S. Y. Hu is an ornamental plant of Hibiscus, native to Taiwan. Here, we reported the complete chloroplast genome of H. taiwanensis. The chloroplast genome of H. taiwanensis was 161,056 bp in length, containing a couple of inverted repeat (IR) regions of 26,300 bp, a large single-copy (LSC) region of 89,538 bp and a small single-copy (SSC) region of 18,918 bp. The complete chloroplast genome annotation revealed a total of 131 genes, including 85 protein-coding genes, 7 rRNA genes, and 37 tRNA genes. The entire GC content was 36.9%. Phylogenetic tree analyses indicated that H. taiwanensis was closely clustered with H. rosa-sinensis and H. syriacus.
Keywords: Hibiscus taiwanensis; chloroplast; genome.
© 2019 The Author(s). Published by Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest and are responsible for the content.
Figures
References
-
- Doyle JJ, Doyle JL. 1987. A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem Bull. 19:11–15.
-
- Gan WS. 1965. Manual of medicinal plants in Taiwan. Vol. 3 Taiwan: National Research Institute of Chinese Medicine; p. 516.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous