The complete chloroplast genome of a medical herb, Halenia elliptica D.Don (Gentianaceae), from Qinghai-Tibet Plateau in China
- PMID: 33366003
- PMCID: PMC7707369
- DOI: 10.1080/23802359.2019.1674202
The complete chloroplast genome of a medical herb, Halenia elliptica D.Don (Gentianaceae), from Qinghai-Tibet Plateau in China
Abstract
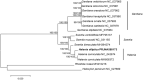
Halenia elliptica D.Don (Gentianaceae) is one of the genuine medicinal species in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Here we report the first chloroplast (cp) genome of H. elliptica using Illumina HiSeq X Ten platform. The length of its complete cp genome is 153,341 bp, containing four sub-regions; a large single-copy region (LSC) of 82,811 bp and a small single-copy region (SSC) of 18,278 bp, which are separated by a pair of inverted repeat regions (IRs) of 26,126bp each. The complete cp genome of H. elliptica contains 129 genes, including 84 protein-coding genes, 37 tRNA genes, and 8 rRNA genes. The overall GC content of the cp genome is 38.1%. The phylogenetic analysis, based on 15 cp genomes, suggested that H. elliptica is closely related to Halenia corniculata (L.) Cornaz and Swertia species.
Keywords: Gentianaceae; Halenia elliptica; Qinghai-Tibet Plateau; chloroplast genome; phylogenetic trees.
© 2019 The Author(s). Published by Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures
References
-
- Bakker FT, Lei D, Yu JY, Mohammadin S, Wei Z, van de Kerke S, Gravendeel B, Nieuwenhuis M, Staats M, Alquezar-Planas DE, et al. 2016. Herbarium genomics: plastome sequence assembly from a range of herbarium specimens using an Iterative Organelle Genome Assembly pipeline. Biol J Linn Soc. 117:33–43.
-
- Chassot P, Nemomissa S, Yuan Y-M, Küpfer P. 2001. High paraphyly of Swertia L. (Gentianaceae) in the Gentianella-lineage as revealed by nuclear and chloroplast DNA sequence variation. Plant Systematics and Evolution. 229:1–21.
-
- Jia MR, Li XW. 2005. Chinese ethnopharmacology. China Medical Science Press; p. 312.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
