Characterization of the complete chloroplast genome of Euphorbia helioscopia Linn. (Euphorbiaceae), a traditional Chinese medicine
- PMID: 33366183
- PMCID: PMC7707446
- DOI: 10.1080/23802359.2019.1682480
Characterization of the complete chloroplast genome of Euphorbia helioscopia Linn. (Euphorbiaceae), a traditional Chinese medicine
Abstract
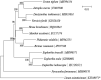
Euphorbia helioscopia Linn. known as a traditional Chinese medicine of Euphorbiaceae, which contains terpenes, steroids, flavonoids, acetophenones, tannins, phenylpropanoids, cerebrosides and so on. Euphorbia helioscopia L. was used to treat malignant tumors and chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases such as cough, phlegm-turbidity, asthma, and chronic bronchitis. The complete chloroplast genome was assembled by Illumina paired-end reads data. The length of circular cp genome distribution in 160,041 bp, containing a large single-copy region (LSC) of 88,832 bp, a small single-copy region (SSC) of 17,145 bp and a pair of inverted repeat (IR) regions of 27,032 bp. In addition, 11 genes possess a single intron, while the other two genes (ycf3, clpP) have a couple of introns. The GC content of entire Euphorbia helioscopia L. cp genome, LSC, SSC and IR regions are 35.9, 33.1, 30.3, and 42.3%, respectively. From the NJ phylogenetic tree analysis showed that Euphorbia helioscopia L. and Euphorbia esula are closely related to each other within the family Euphorbiaceae.
Keywords: Euphorbia helioscopia; Euphorbiaceae; Illumina sequencing; chloroplast genome; phylogenetic analysis.
© 2019 The Author(s). Published by Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest and are solely responsible for the content and writing of this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Chen Y, Tang ZJ, Jiang FX, Zhang XX, Lao AN. 1979. Studies on the active principles of Ze-Qi (Euphorbia helioscopia L.), a drug used for chronic bronchitis (I). Acta Pharm Sin. 14:91–95. - PubMed
-
- Doyle JJ, Doyle JL. 1987. A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem Bull. 19:11–15.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous