The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Hippophae rhamnoides subsp. sinensis
- PMID: 33366837
- PMCID: PMC7748493
- DOI: 10.1080/23802359.2020.1719932
The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Hippophae rhamnoides subsp. sinensis
Abstract
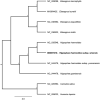
The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Hippophae rahmnoides subsp. sinensis was characterized from Illumina pair-end sequencing. The chloroplast genome of H. rahmnoides subsp. sinensis was 156,355 bp in length, containing a large single-copy region (LSC) of 84,002 bp, a small single-copy region (SSC) of 19,055 bp, and two inverted repeat (IR) regions of 26,649 bp. The overall GC content is 36.6%, while the corresponding values of the LSC, SSC, and IR regions are 64.5%, 69.2%, and 60.1%, respectively. The genome contains 131 complete genes, including 88 protein-coding genes, 38 tRNA genes (29 tRNA species), and 8 rRNA genes (4 rRNA species). The neighbour-joining phylogenetic analysis showed that H. rahmnoides subsp. sinensis and H. rahmnoides clustered together as sisters to other H. rahmnoides species.
Keywords: Hippophae rahmnoides subsp. sinensis; chloroplast genome; genetic information; phylogenetic analysis.
© 2020 The Author(s). Published by Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures
References
-
- Doyle J. 1987. A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem Bull. 19(1):11–15.
-
- He C, Li M, Luo H, Gao G, Zhang J.. 2015. Comprehensive evaluation on drought resistance of Hippophea rhamnoides. Forest Res. 28(5):634–639.
-
- Jia D. R, Abbott R. J, Liu T. L, Mao K. S, Bartish I. V, Liu J. Q.. 2012. Out of the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau: evidence for the origin and dispersal of Eurasian temperate plants from a phylogeographic study of Hippophaë rhamnoides (Elaeagnaceae). New Phytologist. 194(4):1123–1133. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous