The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Amomum villosum Lour
- PMID: 33366865
- PMCID: PMC7748462
- DOI: 10.1080/23802359.2020.1721358
The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Amomum villosum Lour
Abstract
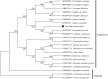
Amomum villosum Lour. (Zingiberaceae) is an important edible and medicinal crop. The complete chloroplast (cp) genome of A. villosum was determined using Illumina sequencing platform. The size of whole cp genome was 164,069 bp, containing a small single copy (SSC) region of 15,353 bp and a large single copy (LSC) region of 88,798 bp, which were separated by a pair of inverted repeat (IRs) regions (29,959 bp). The A. villosum cp genome contained 133 genes, including eight ribosomal RNA genes (4 rRNA species), 38 transfer RNA genes (30 tRNA species) and 87 protein-coding genes (79 PCG species). The overall GC content of A. villosum cp genome is 36.05%. To investigate the evolution status of A. villosum, as well as Zingiberales, a phylogenetic tree with A. villosum and other 21 species was constructed based on their complete chloroplast genomes. Phylogenetic analysis revealed that A. villosum was closely related to Amomum krervanh.
Keywords: Amomum villosum; complete chloroplast genome; phylogenetic analysis.
© 2020 The Author(s). Published by Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures
References
-
- Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission. 2015. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China. Vol. 1. Beijing: China Medical Science and Technology Press; p. 253.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous