The complete mitochondrial genome sequence of Bryopsis plumosa
- PMID: 33366877
- PMCID: PMC7748666
- DOI: 10.1080/23802359.2020.1721031
The complete mitochondrial genome sequence of Bryopsis plumosa
Abstract
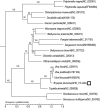
In 2015, a novel macroalgae began to bloom in Qinhuangdao on the coast of the Bohai Sea, Northern China. Bryopsis plumosa, a green macroalga, is one of the causal species of the macroalgae blooms, which have severely affected the environment and ecosystem on the coast of Qinhuangdao. In the present study, we sequenced the mitochondrial genome of B. plumosa for the first time (GenBank accession number MN853874). It was found that the ring-shaped genome was made up of 110,912 base pairs, including 29 protein-coding genes, 23 tRNAs, and 2 rRNAs. Phylogenetic analysis showed B. plumosa had close genetic relationships with algae Ulva prolifera, Ulva linza, and Ulva flexuosa. The present data will provide important information on the phylogenetics and molecular evolution of Bryopsis species.
Keywords: Bryopsis plumosa; Macroalgae blooms; mitochondrial genome; phylogenetic analysis.
© 2020 The Author(s). Published by Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Complete chloroplast genome of Ulva pertusa, one of the causal species of green macroalgal blooms in the coastal waters of Qinhuangdao, China.Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2020 Feb 6;5(1):1084-1086. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2020.1723448. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2020. PMID: 33366885 Free PMC article.
-
Complete mitochondrial genome of Ulva linza, one of the causal species of green macroalgal blooms in Yellow Sea, China.Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2016 Feb 1;1(1):31-33. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2015.1137806. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2016. PMID: 33473396 Free PMC article.
-
Complete mitochondrial genome of Ulva prolifera, the dominant species of green macroalgal blooms in Yellow Sea, China.Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2016 Feb 1;1(1):76-78. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2015.1137831. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2016. PMID: 33473415 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic evidence in tracking the origin of Ulva prolifera blooms in the Yellow Sea, China.Harmful Algae. 2018 Sep;78:86-94. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2018.08.002. Epub 2018 Aug 15. Harmful Algae. 2018. PMID: 30196928 Review.
-
A review of the green tides in the Yellow Sea, China.Mar Environ Res. 2016 Aug;119:189-96. doi: 10.1016/j.marenvres.2016.06.004. Epub 2016 Jun 11. Mar Environ Res. 2016. PMID: 27337549 Review.
References
-
- Liu D, Keesing J, Dong Z, Zhen Y, Di B, Shi Y, Fearns P, Shi P. 2010. Recurrence of Yellow Sea green tide in June 2009 confirms coastal seaweed aquaculture provides nursery for generation of macroalgal blooms. Mar Pollut Bull. 60(9):1423–1432. - PubMed
-
- Liu D, Keesing JK, He P, Wang Z, Shi Y, Wang Y. 2013. The world’s largest macroalgal bloom in the Yellow Sea, China: formation and implications. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci. 129:2–10.
-
- Liu D, Keesing JK, Xing Q, Shi P. 2009. World’s largest macroalgal bloom caused by expansion of seaweed aquaculture in China. Mar Pollut Bull. 58(6):888–895. - PubMed
-
- Schories D, Reise K. 1993. Germination and anchorage of Enteromorpha spp. in sediments of the Wadden Sea. Helgolander Meeresunters. 47(3):275–285.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources