The complete chloroplast genome of Phellodendron chinense (Rutaceae), an Endangered medicinal plant in southern China
- PMID: 33367103
- PMCID: PMC7703704
- DOI: 10.1080/23802359.2020.1837688
The complete chloroplast genome of Phellodendron chinense (Rutaceae), an Endangered medicinal plant in southern China
Abstract
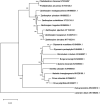
Phellodendron chinense is an Endangered medicinal plant in southern China. In this study, the complete chloroplast genome sequence of P.chinense was characterized by de novo assembly. The length of the whole chloroplast genome was 158,537 bp, containing a large single copy region (LSC) of 86,250 bp and a small single copy region (SSC) of 18,287 bp, which were separated by a pair of 27,000 bp inverted repeat regions (IRs). The sequence contains 114 unique genes, including 30 tRNA, 4 rRNA, and 80 protein-coding genes. The overall GC content of the chloroplast genome is 38.4% and those in the LSC, SSC, and IR regions are 36.6, 33.2, and 42.9%, respectively. The phylogenetic analysis based on reported chloroplast sequences of Rutaceae showed that P. chinense is sister to P. amurense, consisting a monophyletic group, and that Phellodendron is closely related to Zanthoxylum.
Keywords: Phellodendron chinense; chloroplast genome; medicinal plant; phylogeny.
© 2020 The Author(s). Published by Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Bupleurum chinense DC. (Apiaceae).Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2019 Oct 18;4(2):3665-3666. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2019.1678427. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2019. PMID: 33366133 Free PMC article.
-
The complete chloroplast genome of Zanthoxylum piasezkii Maxim. (Rutaceae) and its phylogenetic analysis.Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2021 Feb 5;6(2):306-307. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2020.1866458. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2021. PMID: 33659657 Free PMC article.
-
The first complete chloroplast genome sequence from Polemonium chinense (Polemoniaceae).Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2019 Sep 25;4(2):3214-3215. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2019.1668734. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2019. PMID: 33365925 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of the complete chloroplast genome of Cynanchum acutum subsp. sibiricum (Apocynaceae).Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2023 Sep 19;8(9):993-997. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2023.2256496. eCollection 2023. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2023. PMID: 37746032 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Famous traditional Mongolian medicine Xieriga-4 (Turmeric-4) decoction: A review.Chin Herb Med. 2022 Jul 12;14(3):385-391. doi: 10.1016/j.chmed.2022.05.002. eCollection 2022 Jul. Chin Herb Med. 2022. PMID: 36118011 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Zanthoxylum ailanthoides Sieb. et. Zucc (Rutaceae): an important medicinal plant.Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2024 Apr 12;9(4):506-511. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2024.2338260. eCollection 2024. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2024. PMID: 38623176 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of codon usage bias in chloroplast genomes of ten medicinal species of Rutaceae.BMC Plant Biol. 2024 May 20;24(1):424. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-04999-5. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 38764045 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Appelhans MS, Reichelt N, Groppo M, Paetzold C, Wen J.. 2018. Phylogeny and biogeography of the pantropical genus Zanthoxylum and its closest relatives in the proto-Rutaceae group (Rutaceae). Mol Phylogenet Evol. 126:31–44. - PubMed
-
- Chen LY, Song MS, Zha HG, Li ZM.. 2014. A modified protocol for plant genome DNA extraction. Plant Diversity Resour. 36:375–380.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous