Functional expression of human prostaglandin E2 receptor 4 (EP4) in E. coli and characterization of the binding property of EP4 with Gα proteins
- PMID: 33367116
- PMCID: PMC7749421
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2020.100871
Functional expression of human prostaglandin E2 receptor 4 (EP4) in E. coli and characterization of the binding property of EP4 with Gα proteins
Abstract
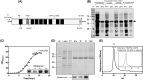
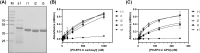
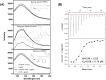
Human prostaglandin E2 receptor 4 (EP4) is one of the four subtypes of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) receptors and belongs to the rhodopsin-type G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) family. Particularly, EP4 is expressed in various cancer cells and is involved in cancer-cell proliferation by a G protein signaling cascade. To prepare an active form of EP4 for biochemical characterization and pharmaceutical application, this study designed a recombinant protein comprising human EP4 fused to the P9 protein (a major envelope protein of phi6 phage) and overexpressed the P9-EP4 fusion protein in the membrane fraction of E. coli. The solubilized P9-EP4 with sarkosyl (a strong anionic detergent) was purified by affinity chromatography. The purified protein was stabilized with amphiphilic polymers derived from poly-γ-glutamate. The polymer-stabilized P9-EP4 showed specific interaction with the alpha subunits of Gs or Gi proteins, and a high content of α-helical structure by a circular dichroism spectroscopy. Furthermore, the polymer-stabilized P9-EP4 showed strong heat resistance compared with P9-EP4 in detergents. The functional preparation of EP4 and its stabilization with amphiphilic polymers could facilitate both the biochemical characterization and pharmacological applications targeting EP4.
Keywords: EP4; G protein; GPCR; Overexpression; PGE2; Purification.
© 2020 The Authors.
Figures

References
-
- Smith W.L., DeWitt D.L., Garavito R.M. Cyclooxygenases: structural, cellular, and molecular biology. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2000;69:145–182. - PubMed
-
- Smith W.L., Marnett L.J., DeWitt D.L. Prostaglandin and thromboxane biosynthesis. Pharmacol. Ther. 1991;49:153–179. - PubMed
-
- Hara S., Kamei D., Sasaki Y., Tanemoto A., Nakatani Y., Murakami M. Prostaglandin E synthases: understanding their pathophysiological roles through mouse genetic models. Biochimie. 2010;92:651–659. - PubMed
-
- Murakami M., Naraba H., Tanioka T., Semmyo N., Nakatani Y., Kojima F., Ikeda T., Fueki M., Ueno A., Oh-ishi S. Regulation of prostaglandin E2 biosynthesis by inducible membrane-associated prostaglandin E2 synthase that acts in concert with cyclooxygenase-2. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:32783–32792. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

