A Tailored High-Efficiency Sample Pretreatment Method for Simultaneous Quantification of 10 Classes of Known Endogenous Phytohormones
- PMID: 33367242
- PMCID: PMC7747986
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xplc.2020.100047
A Tailored High-Efficiency Sample Pretreatment Method for Simultaneous Quantification of 10 Classes of Known Endogenous Phytohormones
Abstract
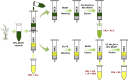
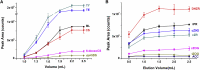
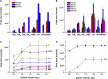
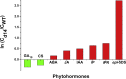
One of the hottest topics in plant hormone biology is the crosstalk mechanisms, whereby multiple classes of phytohormones interplay with each other through signaling networks. To better understand the roles of hormonal crosstalks in their complex regulatory networks, it is of high significance to investigate the spatial and temporal distributions of multiple -phytohormones simultaneously from one plant tissue sample. In this study, we develop a high-sensitivity and high-throughput method for the simultaneous quantitative analysis of 44 phytohormone compounds, covering currently known 10 major classes of phytohormones (strigolactones, brassinosteroids, gibberellins, auxin, abscisic acid, jasmonic acid, salicylic acid, cytokinins, ethylene, and polypeptide hormones [e.g., phytosulfokine]) from only 100 mg of plant sample. These compounds were grouped and purified separately with a tailored solid-phase extraction procedure based on their physicochemical properties and then analyzed by LC-MS/MS. The recoveries of our method ranged from 49.6% to 99.9% and the matrix effects from 61.8% to 102.5%, indicating that the overall sample pretreatment design resulted in good purification. The limits of quantitation (LOQs) of our method ranged from 0.06 to 1.29 pg/100 mg fresh weight and its precision was less than 13.4%, indicating high sensitivity and good reproducibility of the method. Tests of our method in different plant matrices demonstrated its wide applicability. Collectively, these advantages will make our method helpful in clarifying the crosstalk networks of phytohormones.
Keywords: LC–MS/MS; phytohormones; plant tissue; quantitative analysis; solid-phase extraction.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Figures
References
-
- Bari R., Jones J. Role of plant hormones in plant defence responses. Plant Mol. Biol. 2009;69:473–488. - PubMed
-
- Beveridge C.A., Kyozuka J. New genes in the strigolactone-related shoot branching pathway. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2010;13:34–39. - PubMed
-
- Cai W.J., Yu L., Wang W., Sun M.X., Feng Y.Q. Simultaneous determination of multiclass phytohormones in submilligram plant samples by one-pot multifunctional derivatization-assisted liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2019;91:3492–3499. - PubMed
-
- Cao Z.Y., Sun L.H., Mou R.X., Zhang L.P., Lin X.Y., Zhu Z.W., Chen M.X. Profiling of phytohormones and their major metabolites in rice using binary solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A. 2016;1451:67–74. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y., Guo Z., Wang X., Qiu C. Sample preparation. J. Chromatogr. A. 2008;1184:191–219. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

