Crosstalk between Ubiquitination and Other Post-translational Protein Modifications in Plant Immunity
- PMID: 33367245
- PMCID: PMC7748009
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xplc.2020.100041
Crosstalk between Ubiquitination and Other Post-translational Protein Modifications in Plant Immunity
Abstract
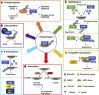
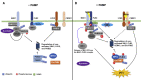
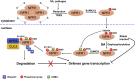
Post-translational modifications (PTMs) are central to the modulation of protein activity, stability, subcellular localization, and interaction with partners. They greatly expand the diversity and functionality of the proteome and have taken the center stage as key players in regulating numerous cellular and physiological processes. Increasing evidence indicates that in addition to a single regulatory PTM, many proteins are modified by multiple different types of PTMs in an orchestrated manner to collectively modulate the biological outcome. Such PTM crosstalk creates a combinatorial explosion in the number of proteoforms in a cell and greatly improves the ability of plants to rapidly mount and fine-tune responses to different external and internal cues. While PTM crosstalk has been investigated in depth in humans, animals, and yeast, the study of interplay between different PTMs in plants is still at its infant stage. In the past decade, investigations showed that PTMs are widely involved and play critical roles in the regulation of interactions between plants and pathogens. In particular, ubiquitination has emerged as a key regulator of plant immunity. This review discusses recent studies of the crosstalk between ubiquitination and six other PTMs, i.e., phosphorylation, SUMOylation, poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation, acetylation, redox modification, and glycosylation, in the regulation of plant immunity. The two basic ways by which PTMs communicate as well as the underlying mechanisms and diverse outcomes of the PTM crosstalk in plant immunity are highlighted.
Keywords: PTM crosstalk; S-nitrosylation; SUMOylation; phosphorylation; plant immunity; ubiquitination.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Figures
References
-
- Ame J.C., Apiou F., Jacobson E.L., Jacobson M.K. Assignment of the poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase gene (PARG) to human chromosome 10q11.23 and mouse chromosome 14B by in situ hybridization. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 1999;85:269–270. - PubMed
-
- Benlloch R., Lois L.M. Sumoylation in plants: mechanistic insights and its role in drought stress. J. Exp. Bot. 2018;69:4539–4554. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

