Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol reduction and statin intensity in myocardial infarction patients and major adverse outcomes: a Swedish nationwide cohort study
- PMID: 33367526
- PMCID: PMC7954251
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa1011
Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol reduction and statin intensity in myocardial infarction patients and major adverse outcomes: a Swedish nationwide cohort study
Abstract
Aims: Clinical trials have demonstrated that a reduction in low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) reduces cardiovascular (CV) events. This has, however, not yet been shown in a real-world setting. We aimed to investigate the association between LDL-C changes and statin intensity with prognosis after a myocardial infarction (MI).
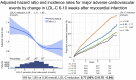
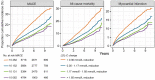
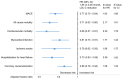
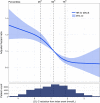
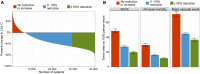
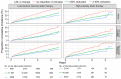
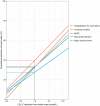
Methods and results: Patients admitted with MI were followed for mortality and major CV events. Changes in LDL-C between the MI and a 6- to 10-week follow-up visit were analysed. The associations between quartiles of LDL-C change and statin intensity with outcomes were assessed using adjusted Cox regression analyses. A total of 40 607 patients were followed for a median of 3.78 years. The median change in LDL-C was a 1.20 mmol/L reduction. Patients with larger LDL-C reduction (1.85 mmol/L, 75th percentile) compared with a smaller reduction (0.36 mmol/L, 25th percentile) had lower hazard ratios (HR) for all outcomes (95% confidence interval): composite of CV mortality, MI, and ischaemic stroke 0.77 (0.70-0.84); all-cause mortality 0.71 (0.63-0.80); CV mortality 0.68 (0.57-0.81); MI 0.81 (0.73-0.91); ischaemic stroke 0.76 (0.62-0.93); heart failure hospitalization 0.73 (0.63-0.85), and coronary artery revascularization 0.86 (0.79-0.94). Patients with ≥50% LDL-C reduction using high-intensity statins at discharge had a lower incidence of all outcomes compared with those using a lower intensity statin.
Conclusions: Larger early LDL-C reduction and more intensive statin therapy after MI were associated with a reduced hazard of all CV outcomes and all-cause mortality. This supports clinical trial data suggesting that earlier lowering of LDL-C after an MI confers the greatest benefit.
Keywords: Cardiovascular mortality; Cardiovascular outcomes; LDL-C; Myocardial infarction; Secondary prevention; Statin.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures
Comment in
-
Changing the paradigm for post-MI cholesterol lowering from intensive statin monotherapy towards intensive lipid-lowering regimens and individualized care.Eur Heart J. 2021 Jan 20;42(3):253-256. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa1008. Eur Heart J. 2021. PMID: 33454778 No abstract available.
References
-
- Borén J, Chapman MJ, Krauss RM, Packard CJ, Bentzon JF, Binder CJ, Daemen MJ, Demer LL, Hegele RA, Nicholls SJ, Nordestgaard BG, Watts GF, Bruckert E, Fazio S, Ference BA, Graham I, Horton JD, Landmesser U, Laufs U, Masana L, Pasterkamp G, Raal FJ, Ray KK, Schunkert H, Taskinen M-R, Sluis BVD, Wiklund O, Tokgozoglu L, Catapano AL, Ginsberg HN.. Low-density lipoproteins cause atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: pathophysiological, genetic, and therapeutic insights: a consensus statement from the European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus Panel. Eur Heart J Oxford Academic 2020;41:2313–2330. - PMC - PubMed
-
- de Lemos JA, Blazing MA, Wiviott SD, Lewis EF, Fox KAA, White HD, Rouleau J-L, Pedersen TR, Gardner LH, Mukherjee R, Ramsey KE, Palmisano J, Bilheimer DW, Pfeffer MA, Califf RM, Braunwald E, Investigators. Early intensive vs a delayed conservative simvastatin strategy in patients with acute coronary syndromes: phase Z of the A to Z trial. JAMA 2004;292:1307–1316. - PubMed
-
- Cannon CP, Blazing MA, Giugliano RP, McCagg A, White JA, Theroux P, Darius H, Lewis BS, Ophuis TO, Jukema JW, De Ferrari GM, Ruzyllo W, De Lucca P, Im K, Bohula EA, Reist C, Wiviott SD, Tershakovec AM, Musliner TA, Braunwald E, Califf RM.. Ezetimibe added to statin therapy after acute coronary syndromes. N Engl J Med 2015;372:2387–2397. - PubMed
-
- Sabatine MS, Giugliano RP, Keech AC, Honarpour N, Wiviott SD, Murphy SA, Kuder JF, Wang H, Liu T, Wasserman SM, Sever PS, Pedersen TR.. Evolocumab and clinical outcomes in patients with cardiovascular disease. N Engl J Med 2017;376:1713–1722. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz GG, Steg PG, Szarek M, Bhatt DL, Bittner VA, Diaz R, Edelberg JM, Goodman SG, Hanotin C, Harrington RA, Jukema JW, Lecorps G, Mahaffey KW, Moryusef A, Pordy R, Quintero K, Roe MT, Sasiela WJ, Tamby J-F, Tricoci P, White HD, Zeiher AM.. Alirocumab and cardiovascular outcomes after acute coronary syndrome. N Engl J Med 2018;379:2097–2107. - PubMed

