Identification of sub-Golgi protein localization by use of deep representation learning features
- PMID: 33367627
- PMCID: PMC8023683
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa1074
Identification of sub-Golgi protein localization by use of deep representation learning features
Abstract
Motivation: The Golgi apparatus has a key functional role in protein biosynthesis within the eukaryotic cell with malfunction resulting in various neurodegenerative diseases. For a better understanding of the Golgi apparatus, it is essential to identification of sub-Golgi protein localization. Although some machine learning methods have been used to identify sub-Golgi localization proteins by sequence representation fusion, more accurate sub-Golgi protein identification is still challenging by existing methodology.
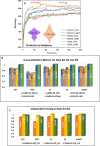
Results: we developed a protein sub-Golgi localization identification protocol using deep representation learning features with 107 dimensions. By this protocol, we demonstrated that instead of multi-type protein sequence feature representation fusion as in previous state-of-the-art sub-Golgi-protein localization classifiers, it is sufficient to exploit only one type of feature representation for more accurately identification of sub-Golgi proteins. Compared with independent testing results for benchmark datasets, our protocol is able to perform generally, reliably and robustly for sub-Golgi protein localization prediction.
Availabilityand implementation: A use-friendly webserver is freely accessible at http://isGP-DRLF.aibiochem.net and the prediction code is accessible at https://github.com/zhibinlv/isGP-DRLF.
Supplementary information: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Identification of plant vacuole proteins by exploiting deep representation learning features.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022 Jun 8;20:2921-2927. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.06.002. eCollection 2022. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 35765653 Free PMC article.
-
GASIDN: identification of sub-Golgi proteins with multi-scale feature fusion.BMC Genomics. 2024 Oct 30;25(1):1019. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10954-3. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39478465 Free PMC article.
-
prPred-DRLF: Plant R protein predictor using deep representation learning features.Proteomics. 2022 Jan;22(1-2):e2100161. doi: 10.1002/pmic.202100161. Epub 2021 Oct 14. Proteomics. 2022. PMID: 34569713
-
Anticancer peptides prediction with deep representation learning features.Brief Bioinform. 2021 Sep 2;22(5):bbab008. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbab008. Brief Bioinform. 2021. PMID: 33529337
-
Exploring sequence-based features for the improved prediction of DNA N4-methylcytosine sites in multiple species.Bioinformatics. 2019 Apr 15;35(8):1326-1333. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty824. Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 30239627
Cited by
-
Prediction of protein solubility based on sequence physicochemical patterns and distributed representation information with DeepSoluE.BMC Biol. 2023 Jan 24;21(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s12915-023-01510-8. BMC Biol. 2023. PMID: 36694239 Free PMC article.
-
SYNBIP: synthetic binding proteins for research, diagnosis and therapy.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Jan 7;50(D1):D560-D570. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab926. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 34664670 Free PMC article.
-
AACFlow: an end-to-end model based on attention augmented convolutional neural network and flow-attention mechanism for identification of anticancer peptides.Bioinformatics. 2024 Mar 4;40(3):btae142. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btae142. Bioinformatics. 2024. PMID: 38452348 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of plant vacuole proteins by exploiting deep representation learning features.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022 Jun 8;20:2921-2927. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.06.002. eCollection 2022. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 35765653 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Predicting Protein S-Nitrosylation Sites.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Feb 9;2021:5542224. doi: 10.1155/2021/5542224. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 33628788 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahmad J. et al. (2019) MFSC: multi-voting based feature selection for classification of Golgi proteins by adopting the general form of Chou's PseAAC components. J. Theor. Biol., 463, 99–109. - PubMed
-
- Ahmad J. et al. (2017) Intelligent computational model for classification of sub-Golgi protein using oversampling and fisher feature selection methods. Artif. Intell. Med., 78, 14–22. - PubMed
-
- Armenteros J.J.A. et al. (2017) DeepLoc: prediction of protein subcellular localization using deep learning. Bioinformatics, 33, 4049–4049. - PubMed
-
- Armenteros J.J.A. et al. (2019) SignalP 5.0 improves signal peptide predictions using deep neural networks. Nat. Biotechnol., 37, 420. - PubMed

