SARS-CoV-2 Serologic Assays in Control and Unknown Populations Demonstrate the Necessity of Virus Neutralization Testing
- PMID: 33367830
- PMCID: PMC7798987
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiaa797
SARS-CoV-2 Serologic Assays in Control and Unknown Populations Demonstrate the Necessity of Virus Neutralization Testing
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to: SARS-CoV-2 Serologic Assays in Control and Unknown Populations Demonstrate the Necessity of Virus Neutralization Testing.J Infect Dis. 2021 Aug 16;224(4):741-745. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiab198. J Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34250540 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: To determine how serologic antibody testing outcome links with virus neutralization of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), we evaluated individuals for SARS-CoV-2 antibody level and viral neutralization.
Methods: We compared serum Ig levels across platforms of viral antigens and antibodies with 15 positive and 30 negative SARS-CoV-2 controls followed by viral neutralization assessment. We then applied these platforms to a clinically relevant cohort of 114 individuals with unknown histories of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
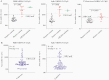
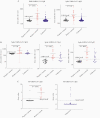
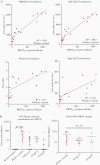
Results: In controls, the best-performing virus-specific antibody detection platforms were SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain (RBD) IgG (sensitivity 87%, specificity 100%, positive predictive value [PPV] 100%, negative predictive value [NPV] 94%), spike IgG3 (sensitivity 93%, specificity 97%, PPV 93%, NPV 97%), and nucleocapsid protein (NP) IgG (sensitivity 93%, specificity 97%, PPV 93%, NPV 97%). Neutralization of positive and negative control sera showed 100% agreement. Twenty individuals with unknown history had detectable SARS-CoV-2 antibodies with 16 demonstrating virus neutralization. Spike IgG3 provided the highest accuracy for predicting serologically positive individuals with virus neutralization activity (misidentified 1/20 unknowns compared to 2/20 for RBD and NP IgG).
Conclusions: The coupling of virus neutralization analysis to a spike IgG3 antibody test is optimal to categorize patients for correlates of SARS-CoV-2 immune protection status.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; antibody; immunity; neutralization; serologic; two-tiered testing.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For permissions, e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures


References
-
- Vandergaast R, Carey T, Reiter S, et al. Development and validation of IMMUNO-COV™: a high-throughput clinical assay for detecting antibodies that neutralize SARS-CoV-2. bioRxiv, doi: 10.1101/2020.05.26.117549, 27. May 2020, preprint: not peer reviewed. - DOI
-
- Breuer J, Schmid DS, Gershon AA. Use and limitations of varicella-zoster virus-specific serological testing to evaluate breakthrough disease in vaccinees and to screen for susceptibility to varicella. J Infect Dis 2008; 197(Suppl 2):S147–51. - PubMed
-
- Gershon AA, Larussa P, Steinberg S. Detection of antibodies to varicella-zoster virus using a latex agglutination assay. Clin Diagn Virol 1994; 2:271–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

