Renal Tubular Acidosis and Management Strategies: A Narrative Review
- PMID: 33367987
- PMCID: PMC7889554
- DOI: 10.1007/s12325-020-01587-5
Renal Tubular Acidosis and Management Strategies: A Narrative Review
Abstract
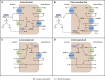
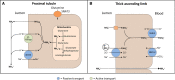
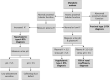
Renal tubular acidosis (RTA) occurs when the kidneys are unable to maintain normal acid-base homeostasis because of tubular defects in acid excretion or bicarbonate ion reabsorption. Using illustrative clinical cases, this review describes the main types of RTA observed in clinical practice and provides an overview of their diagnosis and treatment. The three major forms of RTA are distal RTA (type 1; characterized by impaired acid excretion), proximal RTA (type 2; caused by defects in reabsorption of filtered bicarbonate), and hyperkalemic RTA (type 4; caused by abnormal excretion of acid and potassium in the collecting duct). Type 3 RTA is a rare form of the disease with features of both distal and proximal RTA. Accurate diagnosis of RTA plays an important role in optimal patient management. The diagnosis of distal versus proximal RTA involves assessment of urinary acid and bicarbonate secretion, while in hyperkalemic RTA, selective aldosterone deficiency or resistance to its effects is confirmed after exclusion of other causes of hyperkalemia. Treatment options include alkali therapy in patients with distal or proximal RTA and lowering of serum potassium concentrations through dietary modification and potential new pharmacotherapies in patients with hyperkalemic RTA including newer potassium binders.
Keywords: Alkali therapy; Distal renal tubular acidosis; Hyperkalemic renal tubular acidosis; Normal anion gap metabolic acidosis; Potassium binders; Proximal renal tubular acidosis.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

