Preoperative, Multidisciplinary Clinical Optimization of Patients with Severely Depressed Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction Who Are Undergoing Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting
- PMID: 33367988
- PMCID: PMC8126524
- DOI: 10.1007/s40119-020-00207-1
Preoperative, Multidisciplinary Clinical Optimization of Patients with Severely Depressed Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction Who Are Undergoing Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Preoperative, Multidisciplinary Clinical Optimization of Patients with Severely Depressed Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction Who Are Undergoing Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting.Cardiol Ther. 2021 Dec;10(2):609-610. doi: 10.1007/s40119-021-00235-5. Cardiol Ther. 2021. PMID: 34292505 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
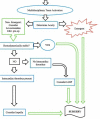
Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) remains a routine operation despite major advancements in angioplastic procedures. Around 200,000 CABG procedures are performed annually in the U.S. Patients who are not candidates for angioplasty intervention often have advanced coronary disease and comorbidities that raise the risk of heart failure with decreased ejection fraction to around 25%. Over the years, significant developments in various preoperative interventions have occurred; in this paper, we suggest a multidisciplinary preoperative algorithm that can be included in a regularly scheduled multidisciplinary care plan.
Keywords: Cardiomyopathy; Coronary artery bypass; Low ejection fraction; Preoperative optimization.
Figures
References
-
- Wolff G, Dimitroulis D, Andreotti F, Kołodziejczak M, Jung C, Scicchitano P, Devito F, Zito A, Occhipinti M, Castiglioni B, Calveri G. Survival benefits of invasive versus conservative strategies in heart failure in patients with reduced ejection fraction and coronary artery disease: a meta-analysis. Circ Heart Fail. 2017;10(1):e003255. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.116.003255. - DOI - PubMed
-
- El Baz N, Middel B, Van Dijk JP, Boonstra PW, Reijneveld SA. Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery patients in a clinical pathway gained less in health-related quality of life as compared with patients who undergo CABG in a conventional-care plan. J Eval Clin Pract. 2009;15(3):498–505. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2753.2008.01051.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources