Risk-mitigating behaviours in people with inflammatory skin and joint disease during the COVID-19 pandemic differ by treatment type: a cross-sectional patient survey
- PMID: 33368145
- PMCID: PMC9214088
- DOI: 10.1111/bjd.19755
Risk-mitigating behaviours in people with inflammatory skin and joint disease during the COVID-19 pandemic differ by treatment type: a cross-sectional patient survey
Abstract
Background: Registry data suggest that people with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs) receiving targeted systemic therapies have fewer adverse coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outcomes compared with patients receiving no systemic treatments.
Objectives: We used international patient survey data to explore the hypothesis that greater risk-mitigating behaviour in those receiving targeted therapies may account, at least in part, for this observation.
Methods: Online surveys were completed by individuals with psoriasis (globally) or rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMDs) (UK only) between 4 May and 7 September 2020. We used multiple logistic regression to assess the association between treatment type and risk-mitigating behaviour, adjusting for clinical and demographic characteristics. We characterized international variation in a mixed-effects model.
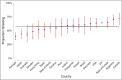
Results: Of 3720 participants (2869 psoriasis, 851 RMDs) from 74 countries, 2262 (60·8%) reported the most stringent risk-mitigating behaviour (classified here under the umbrella term 'shielding'). A greater proportion of those receiving targeted therapies (biologics and Janus Kinase inhibitors) reported shielding compared with those receiving no systemic therapy [adjusted odds ratio (OR) 1·63, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1·35-1·97]. The association between targeted therapy and shielding was preserved when standard systemic therapy was used as the reference group (OR 1·39, 95% CI 1·23-1·56). Shielding was associated with established risk factors for severe COVID-19 [male sex (OR 1·14, 95% CI 1·05-1·24), obesity (OR 1·37, 95% CI 1·23-1·54), comorbidity burden (OR 1·43, 95% CI 1·15-1·78)], a primary indication of RMDs (OR 1·37, 95% CI 1·27-1·48) and a positive anxiety or depression screen (OR 1·57, 95% CI 1·36-1·80). Modest differences in the proportion shielding were observed across nations.
Conclusions: Greater risk-mitigating behaviour among people with IMIDs receiving targeted therapies may contribute to the reported lower risk of adverse COVID-19 outcomes. The behaviour variation across treatment groups, IMIDs and nations reinforces the need for clear evidence-based patient communication on risk-mitigation strategies and may help inform updated public health guidelines as the pandemic continues.
© 2020 The Authors. British Journal of Dermatology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of British Association of Dermatologists.
Figures


Comment in
-
Psoriasis, COVID-19 and shielding.Br J Dermatol. 2021 Jul;185(1):7-8. doi: 10.1111/bjd.20055. Epub 2021 May 5. Br J Dermatol. 2021. PMID: 33951179 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wu Z, McGoogan JM. Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA 2020; 323:1239–42. - PubMed
-
- Onder G, Rezza G, Brusaferro S. Case‐fatality rate and characteristics of patients dying in relation to COVID‐19 in Italy. JAMA 2020; 323:1775–6. - PubMed
-
- Mathur R, Rentsch CT, Morton C et al. Ethnic differences in COVID‐19 infection, hospitalisation, and mortality: an OpenSAFELY analysis of 17 million adults in England. medRXiv 2020; 10.1101/2020.09.22.20198754 (preprint). - DOI
-
- World Health Organization. Tracking public health and social measures. Available at: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel‐coronavirus‐2019/phsm (last accessed 15 Jan 2021).
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

