Spatial and temporal roles of SARS-CoV PLpro -A snapshot
- PMID: 33368679
- PMCID: PMC7883198
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.202002271
Spatial and temporal roles of SARS-CoV PLpro -A snapshot
Abstract
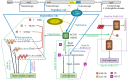
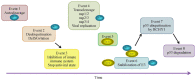
SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 encode four structural and accessory proteins (spike, envelope, membrane and nucleocapsid proteins) and two polyproteins (pp1a and pp1ab). The polyproteins are further cleaved by 3C-like cysteine protease (3CLpro ) and papain-like protease (PLpro ) into 16 nonstructural proteins (nsps). PLpro is released from nsp3 through autocleavage, and then it cleaves the sites between nsp1/2, between nsp2/3 and between nsp3/4 with recognition motif of LXGG, and the sites in the C-terminus of ubiquitin and of protein interferon-stimulated gene 15 (ISG15) with recognition motif of RLRGG. Alone or together with SARS unique domain (SUD), PLpro can stabilize an E3 ubiquitin ligase, the ring-finger, and CHY zinc-finger domain-containing 1 (RCHY1), through domain interaction, and thus, promote RCHY1 to ubiquitinate its target proteins including p53. However, a dilemma appears in terms of PLpro roles. On the one hand, the ubiquitination of p53 is good for SARS-CoV because the ubiquitinated p53 cannot inhibit SARS-CoV replication. On the other hand, the ubiquitination of NF-κB inhibitor (IκBα), TNF receptor-associated factors (TRAFs), and stimulator of interferon gene (STING), and the ISGylation of targeted proteins are bad for SARS-CoV because these ubiquitination and ISGylation initiate the innate immune response and antiviral state. This mini-review analyzes the dilemma and provides a snapshot on how the viral PLpro smartly manages its roles to avoid its simultaneously contradictory actions, which could shed lights on possible strategies to deal with SARS-CoV-2 infections.
Keywords: ISG15; PLpro; SARS-CoV; SARS-CoV-2; p53; ubiquitin.
© 2020 The Authors. The FASEB Journal published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology.
Figures
References
-
- Thiel V, Ivanov KA, Putics Á, et al. Mechanisms and enzymes involved in SARS coronavirus genome expression. J Gen Virol. 2003;84(Pt 9):2305‐2315. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous