Inhibiting CDK4/6 in Breast Cancer with Palbociclib, Ribociclib, and Abemaciclib: Similarities and Differences
- PMID: 33369721
- PMCID: PMC7952354
- DOI: 10.1007/s40265-020-01461-2
Inhibiting CDK4/6 in Breast Cancer with Palbociclib, Ribociclib, and Abemaciclib: Similarities and Differences
Abstract
The cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 4/6 inhibitors belong to a new class of drugs that interrupt proliferation of malignant cells by inhibiting progression through the cell cycle. Three such inhibitors, palbociclib, ribociclib, and abemaciclib were recently approved for breast cancer treatment in various settings and combination regimens. On the basis of their impressive efficacy, all three CDK4/6 inhibitors now play an important role in the treatment of patients with HR+, HER2- breast cancer; however, their optimal use still needs to be established. The three drugs have many similarities in both pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. However, there are some differences on the basis of which the choice for a particular CDK4/6 inhibitor for an individual patient can be important. In this article, the clinical pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profiles of the three CDK4/6 inhibitors are reviewed and important future directions of the clinical applicability of CDK4/6 inhibitors will be discussed.
Conflict of interest statement
Stijn L.W. Koolen has received a research grant from Novartis. C. Louwrens Braal, Elisabeth M. Jongbloed, Saskia M. Wilting, Agnes Jager and Ron H.J. Mathijssen declare they have no conflicts of interest that might be relevant to the contents of this manuscript.
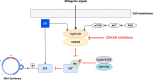
Figures
References
-
- Parise CA, Bauer KR, Brown MM, Caggiano V. Breast cancer subtypes as defined by the estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), and the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) among women with invasive breast cancer in California, 1999–2004. Breast J. 2009;15(6):593–602. - PubMed
-
- Lobbezoo DJA, van Kampen RJW, Voogd AC, Dercksen MW, van den Berkmortel F, Smilde TJ, et al. Prognosis of metastatic breast cancer subtypes: the hormone receptor/HER2-positive subtype is associated with the most favorable outcome. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013;141(3):507–514. - PubMed
-
- Silberholz J, Bertsimas D, Vahdat L. Clinical benefit, toxicity and cost of metastatic breast cancer therapies: systematic review and meta-analysis. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2019;176(3):535–543. - PubMed
-
- Giuliano M, Schettini F, Rognoni C, Milani M, Jerusalem G, Bachelot T, et al. Endocrine treatment versus chemotherapy in postmenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative, metastatic breast cancer: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20(10):1360–1369. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

