Infliximab-induced optic neuritis
- PMID: 33370961
- PMCID: PMC7757444
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2020-236041
Infliximab-induced optic neuritis
Abstract
Antitumour necrosis factor alpha agents are important treatments in many inflammatory conditions including rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis and the inflammatory bowel diseases. However, there have been case reports of optic neuritis and other demyelinating diseases as complications of these agents. This case report presents a patient with ulcerative colitis on infliximab who presented with sudden onset mono-ocular visual field loss and highlights the diagnosis and management of infliximab-induced optic neuritis.
Keywords: biological agents; drugs: CNS (not psychiatric); inflammatory bowel disease; neuroopthalmology; visual pathway.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2020. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
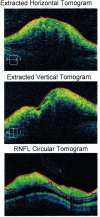
Figures


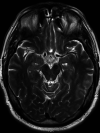
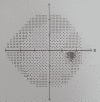

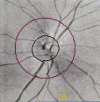
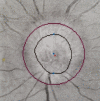

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
