Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of ER Stress Response Reveals both Common and Specific Features in Two Contrasting Ecotypes of Arabidopsis thaliana
- PMID: 33371194
- PMCID: PMC7766468
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21249741
Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of ER Stress Response Reveals both Common and Specific Features in Two Contrasting Ecotypes of Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
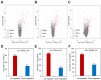
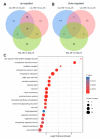
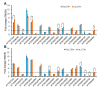
Accumulation of unfolded and misfolded proteins in endoplasmic reticulum (ER) elicits a well-conserved response called the unfolded protein response (UPR), which triggers the upregulation of downstream genes involved in protein folding, vesicle trafficking, and ER-associated degradation (ERAD). Although dynamic transcriptomic responses and the underlying major transcriptional regulators in ER stress response in Arabidopsis have been well established, the proteome changes induced by ER stress have not been reported in Arabidopsis. In the current study, we found that the Arabidopsis Landsberg erecta (Ler) ecotype was more sensitive to ER stress than the Columbia (Col) ecotype. Quantitative mass spectrometry analysis with Tandem Mass Tag (TMT) isobaric labeling showed that, in total, 7439 and 7035 proteins were identified from Col and Ler seedlings, with 88 and 113 differentially regulated (FC > 1.3 or <0.7, p < 0.05) proteins by ER stress in Col and Ler, respectively. Among them, 40 proteins were commonly upregulated in Col and Ler, among which 10 were not upregulated in bzip28 bzip60 double mutant (Col background) plants. Of the 19 specifically upregulated proteins in Col, as compared with that in Ler, components in ERAD, N-glycosylation, vesicle trafficking, and molecular chaperones were represented. Quantitative RT-PCR showed that transcripts of eight out of 19 proteins were not upregulated (FC > 1.3 or <0.7, p < 0.05) by ER stress in Col ecotype, while transcripts of 11 out of 19 proteins were upregulated by ER stress in both ecotypes with no obvious differences in fold change between Col and Ler. Our results experimentally demonstrated the robust ER stress response at the proteome level in plants and revealed differentially regulated proteins that may contribute to the differed ER stress sensitivity between Col and Ler ecotypes in Arabidopsis.
Keywords: Arabidopsis thaliana; ER stress; TMT; UPR; ecotype; proteomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



Similar articles
-
DELLA activity is required for successful pollen development in the Columbia ecotype of Arabidopsis.New Phytol. 2014 Feb;201(3):825-836. doi: 10.1111/nph.12571. Epub 2013 Nov 1. New Phytol. 2014. PMID: 24400898 Free PMC article.
-
A plasma membrane-tethered transcription factor, NAC062/ANAC062/NTL6, mediates the unfolded protein response in Arabidopsis.Plant J. 2014 Sep;79(6):1033-43. doi: 10.1111/tpj.12604. Epub 2014 Jul 30. Plant J. 2014. PMID: 24961665
-
Enhanced nitrate reductase activity offers Arabidopsis ecotype Landsberg erecta better salt stress resistance than Col-0.Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2022 Aug;24(5):854-862. doi: 10.1111/plb.13420. Epub 2022 Mar 31. Plant Biol (Stuttg). 2022. PMID: 35357062
-
Functional Diversification of ER Stress Responses in Arabidopsis.Trends Biochem Sci. 2020 Feb;45(2):123-136. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2019.10.008. Epub 2019 Nov 18. Trends Biochem Sci. 2020. PMID: 31753702 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Multifaceted Roles of Plant Hormone Salicylic Acid in Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Unfolded Protein Response.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Nov 21;20(23):5842. doi: 10.3390/ijms20235842. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31766401 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Proteome and Metabolome Analyses of Albino Bracts in Davidia involucrata.Plants (Basel). 2025 Feb 11;14(4):549. doi: 10.3390/plants14040549. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40006808 Free PMC article.
-
DAP1 regulates osteoblast autophagy via the ATG16L1-LC3 axis in Graves' disease-induced osteoporosis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2023 Sep 21;18(1):711. doi: 10.1186/s13018-023-04171-z. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023. PMID: 37735431 Free PMC article.
-
TMT-based proteomic analysis reveals integrins involved in the synergistic infection of reticuloendotheliosis virus and avian leukosis virus subgroup J.BMC Vet Res. 2022 Apr 4;18(1):131. doi: 10.1186/s12917-022-03207-6. BMC Vet Res. 2022. PMID: 35379256 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic Response of Paracoccidioides brasiliensis Exposed to the Antifungal 4-Methoxynaphthalene-N-acylhydrazone Reveals Alteration in Metabolism.J Fungi (Basel). 2022 Dec 31;9(1):66. doi: 10.3390/jof9010066. J Fungi (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36675887 Free PMC article.
-
The Endoplasmic Reticulum Role in the Plant Response to Abiotic Stress.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Nov 18;12:755447. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.755447. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34868142 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

