Molecular Epidemiology of HIV-1 in African Countries: A Comprehensive Overview
- PMID: 33371264
- PMCID: PMC7766877
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens9121072
Molecular Epidemiology of HIV-1 in African Countries: A Comprehensive Overview
Abstract
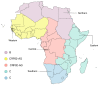
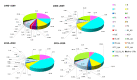
The human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) originated in non-human primates in West-central Africa and continues to be a major global public health issue, having claimed almost 33 million lives so far. In Africa, it is estimated that more than 20 million people are living with HIV/Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) and that more than 730,000 new HIV-1 infections still occur each year, likely due to low access to testing. The high genetic variability of HIV-1, due to a fast replication cycle and high mutation rate, may cause the generation of many viral variants in a single infected patient during a single day. Therefore, the active monitoring and characterization of the HIV-1 subtypes and recombinant forms circulating through African countries poses a significant challenge to more specific diagnoses, treatments, care, and intervention strategies. In this review, a concise characterization of all the subtypes and recombinant forms circulating in Africa is presented to highlight the magnitude of the HIV-1 threat among the African countries and to understand virus genetic diversity and dispersion dynamics better.
Keywords: Africa; HIV-1; circulating recombinant form (CRF); recombinant; subtypes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Global Report 2020. UNAIDS Report on the Global AIDS Epidemic 2020. [(accessed on 10 November 2020)]; UNAIDS Web Site. Available online: https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/fact-sheet.
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) [(accessed on 10 November 2020)]; Available online: https://www.afro.who.int/health-topics/hivaids.
-
- Rueda S., Mitra S., Chen S., Gogolishvili D., Globerman J., Chambers L., Wilson M., Logie C.H., Shi Q., Morassaei S., et al. Examining the associations between HIV-related stigma and health outcomes in people living with HIV/AIDS: A series of meta-analyses. BMJ Open. 2016;6:e011453. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2016-011453. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

