Effects of Chronic Kidney Disease and Uremic Toxins on Extracellular Vesicle Biology
- PMID: 33371311
- PMCID: PMC7767379
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins12120811
Effects of Chronic Kidney Disease and Uremic Toxins on Extracellular Vesicle Biology
Abstract
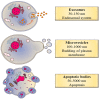
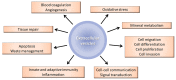
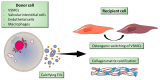
Vascular calcification (VC) is a cardiovascular complication associated with a high mortality rate, especially in patients with diabetes, atherosclerosis or chronic kidney disease (CKD). In CKD patients, VC is associated with the accumulation of uremic toxins, such as indoxyl sulphate or inorganic phosphate, which can have a major impact in vascular remodeling. During VC, vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) undergo an osteogenic switch and secrete extracellular vesicles (EVs) that are heterogeneous in terms of their origin and composition. Under physiological conditions, EVs are involved in cell-cell communication and the maintenance of cellular homeostasis. They contain high levels of calcification inhibitors, such as fetuin-A and matrix Gla protein. Under pathological conditions (and particularly in the presence of uremic toxins), the secreted EVs acquire a pro-calcifying profile and thereby act as nucleating foci for the crystallization of hydroxyapatite and the propagation of calcification. Here, we review the most recent findings on the EVs' pathophysiological role in VC, the impact of uremic toxins on EV biogenesis and functions, the use of EVs as diagnostic biomarkers and the EVs' therapeutic potential in CKD.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; extracellular vesicles; uremic toxins; vascular calcification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of Uremic Toxins in Early Vascular Ageing and Calcification.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Jan 3;13(1):26. doi: 10.3390/toxins13010026. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33401534 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic Kidney Disease Circulating Calciprotein Particles and Extracellular Vesicles Promote Vascular Calcification: A Role for GRP (Gla-Rich Protein).Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018 Mar;38(3):575-587. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.117.310578. Epub 2018 Jan 4. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2018. PMID: 29301790
-
Contribution of Gut Microbiota-Derived Uremic Toxins to the Cardiovascular System Mineralization.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Apr 10;13(4):274. doi: 10.3390/toxins13040274. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33920096 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Uremic Vascular Calcification: The Pathogenic Roles and Gastrointestinal Decontamination of Uremic Toxins.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Dec 21;12(12):812. doi: 10.3390/toxins12120812. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33371477 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vascular pathologies in chronic kidney disease: pathophysiological mechanisms and novel therapeutic approaches.J Mol Med (Berl). 2021 Mar;99(3):335-348. doi: 10.1007/s00109-021-02037-7. Epub 2021 Jan 22. J Mol Med (Berl). 2021. PMID: 33481059 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hallmarks for Thrombotic and Hemorrhagic Risks in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 9;25(16):8705. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168705. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201390 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Fatal Role of Enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli Shiga Toxin-associated Extracellular Vesicles in Host Cells.J Microbiol. 2023 Aug;61(8):715-727. doi: 10.1007/s12275-023-00066-0. Epub 2023 Sep 4. J Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37665555 Review.
-
Pathogenesis and Mechanism of Uremic Vascular Calcification.Cureus. 2024 Jul 17;16(7):e64771. doi: 10.7759/cureus.64771. eCollection 2024 Jul. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39026575 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicles From LPS-Treated Macrophages Aggravate Smooth Muscle Cell Calcification by Propagating Inflammation and Oxidative Stress.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Mar 9;10:823450. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.823450. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35356285 Free PMC article.
-
The Contribution of Extracellular Vesicles From Senescent Endothelial and Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells to Vascular Calcification.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Apr 15;9:854726. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.854726. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35498012 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical