Distant Organ Damage in Acute Brain Injury
- PMID: 33371363
- PMCID: PMC7767338
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci10121019
Distant Organ Damage in Acute Brain Injury
Abstract
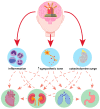
Acute brain injuries pose a great threat to global health, having significant impact on mortality and disability. Patients with acute brain injury may develop distant organ failure, even if no systemic diseases or infection is present. The severity of non-neurologic organs' dysfunction depends on the extremity of the insult to the brain. In this comprehensive review we sought to describe the organ-related consequences of acute brain injuries. The clinician should always be aware of the interplay between central nervous system and non-neurological organs, that is constantly present. Cerebral injury is not only a brain disease, but also affects the body as whole, and thus requires holistic therapeutical approach.
Keywords: acute brain injury; critical illness; organ dysfunction; systemic response.
Conflict of interest statement
acute brain injury; organ dysfunction; critical illness; systemic response
Figures

Similar articles
-
Non-neurologic organ dysfunction in acute brain injury.Crit Care Clin. 2006 Oct;22(4):753-66; abstract x. doi: 10.1016/j.ccc.2006.09.002. Crit Care Clin. 2006. PMID: 17239753 Review.
-
Risk factors for organ dysfunction and failure in patients with acute traumatic cervical spinal cord injury.Neurocrit Care. 2010 Aug;13(1):29-39. doi: 10.1007/s12028-010-9359-9. Neurocrit Care. 2010. PMID: 20407933
-
Distant organ dysfunction in acute kidney injury.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2020 Feb;228(2):e13357. doi: 10.1111/apha.13357. Epub 2019 Sep 3. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2020. PMID: 31379123 Review.
-
Acute kidney injury and distant organ dysfunction-network system analysis.Kidney Int. 2023 Jun;103(6):1041-1055. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2023.03.025. Epub 2023 Apr 6. Kidney Int. 2023. PMID: 37030663 Review.
-
Non-neurological organ dysfunction in neurocritical care: impact on outcome and etiological considerations.Curr Opin Crit Care. 2005 Apr;11(2):139-43. doi: 10.1097/01.ccx.0000155356.86241.c0. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2005. PMID: 15758594 Review.
Cited by
-
Hypoxia-Induced Pulmonary Injury-Adrenergic Blockade Attenuates Nitrosative Stress, and Proinflammatory Cytokines but Not Pulmonary Edema.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2024 Jun 27;11(7):195. doi: 10.3390/jcdd11070195. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2024. PMID: 39057617 Free PMC article.
-
Interorgan communication in neurogenic heterotopic ossification: the role of brain-derived extracellular vesicles.Bone Res. 2024 Feb 22;12(1):11. doi: 10.1038/s41413-023-00310-8. Bone Res. 2024. PMID: 38383487 Free PMC article.
-
Fast Maturation of Splenic Dendritic Cells Upon TBI Is Associated With FLT3/FLT3L Signaling.Front Immunol. 2022 Feb 24;13:824459. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.824459. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35281004 Free PMC article.
-
Risk factors and outcomes associated with systolic dysfunction following traumatic brain injury.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Jul 26;103(30):e38891. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038891. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39058835 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Developments in Mouse Trauma Research Models: A Mini-Review.Front Physiol. 2022 Apr 29;13:866617. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.866617. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35574493 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- WHO Causes of Death. [(accessed on 13 November 2020)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/data/gho/data/themes/topics/causes-of-death.
-
- Sharma R., Shultz S.R., Robinson M.J., Belli A., Hibbs M.L., O’Brien T.J., Semple B.D. Infections after a traumatic brain injury: The complex interplay between the immune and neurological systems. Brain Behav. Immun. 2019;79:63–74. - PubMed
-
- Agrawal A., Reddy P.A., Prasad N.R. Endocrine manifestations of traumatic brain injury. Indian J. Neurotrauma. 2012;9:123–128.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

