The Regulation of Fat Metabolism During Aerobic Exercise
- PMID: 33371437
- PMCID: PMC7767423
- DOI: 10.3390/biom10121699
The Regulation of Fat Metabolism During Aerobic Exercise
Abstract
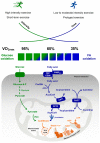
Since the lipid profile is altered by physical activity, the study of lipid metabolism is a remarkable element in understanding if and how physical activity affects the health of both professional athletes and sedentary subjects. Although not fully defined, it has become clear that resistance exercise uses fat as an energy source. The fatty acid oxidation rate is the result of the following processes: (a) triglycerides lipolysis, most abundant in fat adipocytes and intramuscular triacylglycerol (IMTG) stores, (b) fatty acid transport from blood plasma to muscle sarcoplasm, (c) availability and hydrolysis rate of intramuscular triglycerides, and (d) transport of fatty acids through the mitochondrial membrane. In this review, we report some studies concerning the relationship between exercise and the aforementioned processes also in light of hormonal controls and molecular regulations within fat and skeletal muscle cells.
Keywords: endurance exercise; high-density lipoprotein (HDL); lipid metabolism; lipoprotein; low-density lipoprotein (LDL); plasma fatty acids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Soci U.P.R., Melo S.F.S., Gomes J.L.P., Silveira A.C., Nóbrega C., de Oliveira E.M. Exercise training and epigenetic regulation: Multilevel modification and regulation of gene expression. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017;1000:281–322. - PubMed
-
- Mendonca G.V., Pezarat-Correia P., Vaz J.R., Silva L., Almeida I.D., Heffernan K.S. Impact of exercise training on physiological measures of physical fitness in the elderly. Curr. Aging Sci. 2016;9:240–259. - PubMed
-
- Hansen D., de Strijcker D., Calders P. Impact of endurance exercise training in the fasted state on muscle biochemistry and metabolism in healthy subjects: Can these effects be of particular clinical benefit to type 2 diabetes mellitus and insulin-resistant patients? Sports Med. 2017;47:415–428. - PubMed
-
- Bhati P., Shenoy S., Hussain M.E. Exercise training and cardiac autonomic function in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2018;12:69–78. - PubMed
-
- Berlin J.A., Colditz G.A. A meta-analysis of physical activity in the prevention of coronary heart disease. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1990;132:612–628. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

