Gallic acid-gold nanoparticles enhance radiation-induced cell death of human glioma U251 cells
- PMID: 33372372
- PMCID: PMC7898864
- DOI: 10.1002/iub.2436
Gallic acid-gold nanoparticles enhance radiation-induced cell death of human glioma U251 cells
Abstract
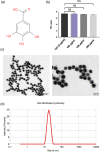
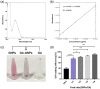
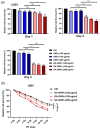
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is among the most common adult brain tumors with invariably fatal character. Following the limited conventional therapies, almost all patients, however, presented with symptoms at the time of recurrence. It is dire to develop novel therapeutic strategies to improve the current treatment of GBM. Gallic acid is a well-established antioxidant, presenting a promising new selective anti-cancer drug, while gold nanoparticles (GNPs) can be developed as versatile nontoxic carriers for anti-cancer drug delivery. Here, we prepared gallic acid-GNPs (GA-GNPs) by loading gallic acid onto GNPs, reduction products of tetrachloroauric acid by sodium citrate, through physical and agitation adsorption. GA-GNPs, rather than GNPs alone, significantly inhibited the survival of U251 GBM cells, as well as enhanced radiation-induced cell death. Moreover, GA-GNPs plus radiation arrested the cell cycle of U251 at the S and G2/M phases and triggered apoptotic cell death, which is supported by increased BAX protein levels and decreased expression of BCL-2. Thus, GA-GNPs have great potential in the combination with radiation therapy in future studies for GBM treatment.
Keywords: gallic acid; glioma; gold nanoparticles; radiotherapy.
© 2020 The Authors. IUBMB Life published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.
Figures

References
-
- Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5‐year analysis of the EORTC‐NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10(5):459–466. - PubMed
-
- Brandes AA, Tosoni A, Franceschi E, et al. Recurrence pattern after temozolomide concomitant with and adjuvant to radiotherapy in newly diagnosed patients with glioblastoma: Correlation with MGMT promoter methylation status. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(8):1275–1279. - PubMed
-
- Galati G, O'Brien PJ. Potential toxicity of flavonoids and other dietary phenolics: Significance for their chemopreventive and anticancer properties. Free Radic Biol Med. 2004;37(3):287–303. - PubMed
-
- Verma S, Singh A, Mishra A. Gallic acid: Molecular rival of cancer. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2013;35(3):473–485. - PubMed
-
- Rasool M, Malik A, Manan A, et al. Roles of natural compounds from medicinal plants in cancer treatment: Structure and mode of action at molecular level. Med Chem. 2015;11(7):618–628. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

