Resting-state functional connectivity and quantitation of glutamate and GABA of the PCC/precuneus by magnetic resonance spectroscopy at 7T in healthy individuals
- PMID: 33373387
- PMCID: PMC7771854
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0244491
Resting-state functional connectivity and quantitation of glutamate and GABA of the PCC/precuneus by magnetic resonance spectroscopy at 7T in healthy individuals
Abstract
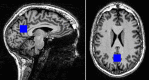
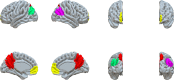
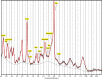
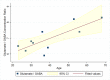
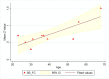
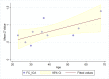
The default mode network (DMN) is the main large-scale network of the resting brain and the PCC/precuneus is a major hub of this network. Glutamate and GABA (γ-amino butyric acid) are the main excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters in the CNS, respectively. We studied glutamate and GABA concentrations in the PCC/precuneus via magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) at 7T in relation to age and correlated them with functional connectivity between this region and other DMN nodes in ten healthy right-handed volunteers ranging in age between 23-68 years. Mean functional connectivity of the PCC/precuneus to the other DMN nodes and the glutamate/GABA ratio significantly correlated with age (r = 0.802, p = 0.005 and r = 0.793, p = 0.006, respectively) but not with each other. Glutamate and GABA alone did not significantly correlate with age nor with functional connectivity within the DMN. The glutamate/GABA ratio and functional connectivity of the PCC/precuneus are, therefore, independent age-related biomarkers of the DMN and may be combined in a multimodal pipeline to study DMN alterations in various disease states.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Khalsa S, Mayhew SD, Chechlacz M, Bagary M, Bagshaw AP. The structural and functional connectivity of the posterior cingulate cortex: Comparison between deterministic and probabilistic tractography for the investigation of structure-function relationships. Neuroimage. 2014;102: 118–127. 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.12.022 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

