Serum IgG2 antibody multicomposition in systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis (Part 1): cross-sectional analysis
- PMID: 33374003
- PMCID: PMC8487649
- DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaa767
Serum IgG2 antibody multicomposition in systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis (Part 1): cross-sectional analysis
Abstract
Objectives: Serum anti-dsDNA and anti-nucleosome IgGs have been proposed as signatures for SLE and LN in limited numbers of patients. We sought to show higher sensitivity and specificity of the same antibodies with the IgG2 isotype and included IgG2 antibodies vs specific intracellular antigens in the analysis.
Methods: A total of 1052 SLE patients with (n = 479) and without (n = 573) LN, recruited at different times from the beginning of symptoms, were included in the study. Patients with primary APS (PAPS, n = 24), RA (RA, n = 24) and UCTD (UCTD, n = 96) were analysed for comparison. Anti-nucleosome (dsDNA, Histone2A, Histone3), anti-intracellular antigens (ENO1), anti-annexin A1 and anti-C1q IgG2 were determined by non-commercial techniques.
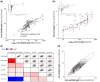
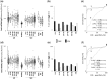
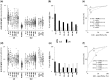
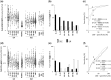
Results: The presence in the serum of the IgG2 panel was highly discriminatory for SLE/LN vs healthy subjects. Serum levels of anti-dsDNA and anti-C1q IgG2 were more sensitive than those of IgGs (Farr radioimmunoassay/commercial assays) in identifying SLE patients at low-medium increments. Of more importance, serum positivity for anti-ENO1 and anti-H2A IgG2 discriminated between LN and SLE (ROC T0-12 months), and high levels at T0-1 month were detected in 63% and 67%, respectively, of LN, vs 3% and 3%, respectively, of SLE patients; serum positivity for each of these was correlated with high SLEDAI values. Minor differences existed between LN/SLE and the other rheumatologic conditions.
Conclusion: Nephritogenic IgG2 antibodies represent a specific signature of SLE/LN, with a few overlaps with other rheumatologic conditions. High levels of anti-ENO1 and anti-H2A IgG2 correlated with SLE activity indexes and were discriminatory between SLE patients limited to the renal complication and other SLE patients.
Trial registration: The Zeus study was registered at https://clinicaltrials.gov, NCT02403115.
Keywords: LN; SLE; anti-C1q antibodies; anti-ENO1 antibodies; anti-Histone 2A antibodies; biomarkers.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Rheumatology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Serum IgG2 antibody multi-composition in systemic lupus erythematosus and in lupus nephritis (Part 2): prospective study.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021 Jul 1;60(7):3388-3397. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaa793. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021. PMID: 33351137 Free PMC article.
-
Glomerular autoimmune multicomponents of human lupus nephritis in vivo: α-enolase and annexin AI.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014 Nov;25(11):2483-98. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2013090987. Epub 2014 May 1. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 24790181 Free PMC article.
-
Association of anti-nuclesome and anti C1q antibodies with lupus nephritis in an Egyptian cohort of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.Adv Rheumatol. 2019 Mar 4;59(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s42358-019-0054-z. Adv Rheumatol. 2019. PMID: 30832710
-
A critical view on autoantibodies in lupus nephritis: Concrete knowledge based on evidence.Autoimmun Rev. 2024 May;23(5):103535. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2024.103535. Epub 2024 Mar 27. Autoimmun Rev. 2024. PMID: 38552995 Review.
-
[Role of the nucleosome in the physiopathology of systemic lupus erythematosus].Ann Med Interne (Paris). 2003 Feb;154(1):25-32. Ann Med Interne (Paris). 2003. PMID: 12746656 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in the Autoimmunity Context.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Mar 22;8:614829. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.614829. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33829021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Relationship between anti-ENO1 antibody and systemic lupus erythematosus patients with retinopathy].Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022 Dec 18;54(6):1099-1105. doi: 10.19723/j.issn.1671-167X.2022.06.007. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022. PMID: 36533339 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Mechanisms Limiting Renal Tissue Protection and Repair in Glomerulonephritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 5;24(9):8318. doi: 10.3390/ijms24098318. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37176025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Technology Innovation for Discovering Renal Autoantibodies in Autoimmune Conditions.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 25;25(23):12659. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312659. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lupus Nephritis Biomarkers: A Critical Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 9;25(2):805. doi: 10.3390/ijms25020805. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38255879 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rahman A, Isenberg DA.. Systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med 2008;358:929–39. - PubMed
-
- Houssiau FA, Vasconcelos C, D’Cruz D. et al.Immunosuppressive therapy in lupus nephritis: the Euro-Lupus Nephritis Trial, a randomized trial of low-dose versus high-dose intravenous cyclophosphamide. Arthritis Rheum 2002;46:2121–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

