GPER1 and microRNA: Two Players in Breast Cancer Progression
- PMID: 33374170
- PMCID: PMC7795792
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22010098
GPER1 and microRNA: Two Players in Breast Cancer Progression
Abstract
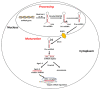
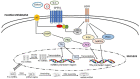
Breast cancer is the main cause of morbidity and mortality in women worldwide. However, the molecular pathogenesis of breast cancer remains poorly defined due to its heterogeneity. Several studies have reported that G Protein-Coupled Estrogen Receptor 1 (GPER1) plays a crucial role in breast cancer progression, by binding to estrogens or synthetic agonists, like G-1, thus modulating genes involved in diverse biological events, such as cell proliferation, migration, apoptosis, and metastasis. In addition, it has been established that the dysregulation of short sequences of non-coding RNA, named microRNAs (miRNAs), is involved in various pathophysiological conditions, including breast cancer. Recent evidence has indicated that estrogens may regulate miRNA expression and therefore modulate the levels of their target genes, not only through the classical estrogen receptors (ERs), but also activating GPER1 signalling, hence suggesting an alternative molecular pathway involved in breast tumor progression. Here, the current knowledge about GPER1 and miRNA action in breast cancer is recapitulated, reporting recent evidence on the liaison of these two players in triggering breast tumorogenic effects. Elucidating the role of GPER1 and miRNAs in breast cancer might provide new tools for innovative approaches in anti-cancer therapy.
Keywords: CAFs; GPER1; breast cancer; estrogens; miRNAs; microRNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
GPER1 influences cellular homeostasis and cytostatic drug resistance via influencing long chain ceramide synthesis in breast cancer cells.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2019 Jul;112:95-106. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2019.05.002. Epub 2019 May 11. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31082617
-
Stabilization of MORC2 by estrogen and antiestrogens through GPER1- PRKACA-CMA pathway contributes to estrogen-induced proliferation and endocrine resistance of breast cancer cells.Autophagy. 2020 Jun;16(6):1061-1076. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2019.1659609. Epub 2019 Sep 6. Autophagy. 2020. PMID: 32401166 Free PMC article.
-
G protein-coupled estrogen receptor is apoptotic and correlates with increased distant disease-free survival of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer patients.Clin Cancer Res. 2013 Apr 1;19(7):1681-92. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-2376. Clin Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23554355
-
Dysregulation of miRNAs as a signature for diagnosis and prognosis of gastric cancer and their involvement in the mechanism underlying gastric carcinogenesis and progression.IUBMB Life. 2020 May;72(5):884-898. doi: 10.1002/iub.2259. Epub 2020 Feb 20. IUBMB Life. 2020. PMID: 32078236 Review.
-
Breast cancer and microRNAs: therapeutic impact.Breast. 2011 Oct;20 Suppl 3:S63-70. doi: 10.1016/S0960-9776(11)70297-1. Breast. 2011. PMID: 22015296 Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive analysis of a new immune-related prognostic signature for esophageal cancer and its correlation with infiltrating immune cells and target genes.Ann Transl Med. 2021 Oct;9(20):1576. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-4756. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34790782 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of MiRNA-29b and MiRNA-31 and their diagnostic and prognostic values in Egyptian females with breast cancer.Noncoding RNA Res. 2022 Sep 6;7(4):248-257. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2022.09.003. eCollection 2022 Dec. Noncoding RNA Res. 2022. PMID: 36247409 Free PMC article.
-
Tailoring Potential Natural Compounds for the Treatment of Luminal Breast Cancer.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Oct 16;16(10):1466. doi: 10.3390/ph16101466. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37895937 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overview of the therapeutic strategies for ER positive breast cancer.Biochem Pharmacol. 2023 Jun;212:115552. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115552. Epub 2023 Apr 15. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37068524 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Different Expression Pattern of G Protein-Coupled Estrogen Receptor GPER1 in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Adenocarcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 13;24(18):14055. doi: 10.3390/ijms241814055. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762356 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Globocan Estimated Cancer Incidence, Mortality et Prevalence Worldwide in 2018. [(accessed on 23 December 2020)];2018 Available online: http://globocan.iarc.fr/Default.aspx.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

