Similarities and Differences in Extracellular Vesicle Profiles between Ischaemic Stroke and Myocardial Infarction
- PMID: 33374290
- PMCID: PMC7824002
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines9010008
Similarities and Differences in Extracellular Vesicle Profiles between Ischaemic Stroke and Myocardial Infarction
Abstract
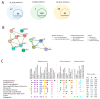
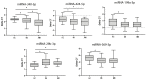
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are involved in intercellular signalling through the transfer of molecules during physiological and pathological conditions, such as ischaemic disease. EVs might therefore play a role in ischaemic stroke (IS) and myocardial infarction (MI). In the present study, we analysed the similarities and differences in the content of circulating EVs in patients with IS and MI. This prospective observational study enrolled 140 participants (81 patients with IS, 37 with MI and 22 healthy controls [HCs]). We analysed the protein and microRNA content from EVs using proteomics and reverse transcription quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction and compared it between the groups. In the patients with IS and MI, we identified 14 common proteins. When comparing IS and MI, we found differences in the protein profiles (apolipoprotein B, alpha-2-macroglobulin, fibronectin). We also found lower levels of miR-340 and miR-424 and higher levels of miR-29b in the patients with IS and MI compared with the HCs. Lastly, we found higher miR-340 levels in IS than in MI. In conclusion, proteomic and miRNA analyses suggest a relationship between circulating EV content and the patient's disease state. Although IS and MI affect different organs (brain and heart) with distinct histological characteristics, certain EV proteins and miRNAs appear to participate in both diseases, while others are present only in patients with IS.
Keywords: exosomes; extracellular vesicles; ischaemia; miRNAs; myocardial infarction; proteins; stroke.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have any potential conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Circulating Extracellular Vesicle Proteins and MicroRNA Profiles in Subcortical and Cortical-Subcortical Ischaemic Stroke.Biomedicines. 2021 Jul 7;9(7):786. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9070786. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34356850 Free PMC article.
-
Stroke severity shapes extracellular vesicle profiles and their impact on the cerebral endothelial cells.J Physiol. 2025 Jan 6. doi: 10.1113/JP285907. Online ahead of print. J Physiol. 2025. PMID: 39761232
-
Beta cell extracellular vesicle miR-21-5p cargo is increased in response to inflammatory cytokines and serves as a biomarker of type 1 diabetes.Diabetologia. 2018 May;61(5):1124-1134. doi: 10.1007/s00125-018-4559-5. Epub 2018 Feb 14. Diabetologia. 2018. PMID: 29445851 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicle miRNAs in the Promotion of Cardiac Neovascularisation.Front Physiol. 2020 Sep 25;11:579892. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.579892. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 33101061 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of exosomes and microvesicles in hypoxia-associated tumour development and cardiovascular disease.J Intern Med. 2015 Sep;278(3):251-63. doi: 10.1111/joim.12393. Epub 2015 Jul 8. J Intern Med. 2015. PMID: 26153525 Review.
Cited by
-
Characterization of Exosomes and Exosomal RNAs Isolated from Post-Mortem Body Fluids for Molecular Forensic Diagnosis.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Sep 5;12(9):2153. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12092153. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36140554 Free PMC article.
-
Recovery After Stroke: New Insight to Promote Brain Plasticity.Front Neurol. 2021 Nov 19;12:768958. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.768958. eCollection 2021. Front Neurol. 2021. PMID: 34867756 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Extracellular vesicles and their microRNA cargo in ischaemic stroke.J Physiol. 2023 Nov;601(22):4907-4921. doi: 10.1113/JP282050. Epub 2022 Apr 28. J Physiol. 2023. PMID: 35421904 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating Extracellular Vesicle Proteins and MicroRNA Profiles in Subcortical and Cortical-Subcortical Ischaemic Stroke.Biomedicines. 2021 Jul 7;9(7):786. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9070786. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34356850 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebral derailment after myocardial infarct: mechanisms and effects of the signaling from the ischemic heart to brain.J Mol Med (Berl). 2022 Jan;100(1):23-41. doi: 10.1007/s00109-021-02154-3. Epub 2021 Oct 21. J Mol Med (Berl). 2022. PMID: 34674004 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization Neurological Disorders. [(accessed on 15 March 2020)]; Available online: http://www.who.int/mental_health/neurology/neurodiso/en/
-
- World Health Organization Cardiovascular Diseases. [(accessed on 15 March 2020)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/cardiovascular-diseases#tab=tab_1.
-
- Van Kralingen J.C., McFall A., Ord E.N.J., Coyle T.F., Bissett M., McClure J.D., McCabe C., Macrae I.M., Dawson J., Work L.M. Altered Extracellular Vesicle MicroRNA Expression in Ischemic Stroke and Small Vessel Disease. Transl. Stroke Res. 2019;10:495–508. doi: 10.1007/s12975-018-0682-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

