Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Bicalutamide Analogues for the Potential Treatment of Prostate Cancer
- PMID: 33374450
- PMCID: PMC7795644
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26010056
Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Bicalutamide Analogues for the Potential Treatment of Prostate Cancer
Abstract
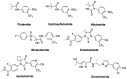
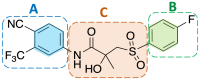
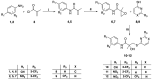
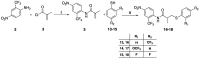
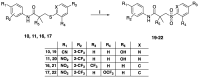
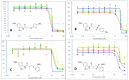
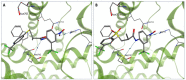
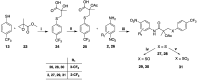
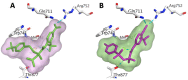
The androgen receptor (AR) is a pivotal target for the treatment of prostate cancer (PC) even when the disease progresses toward androgen-independent or castration-resistant forms. In this study, a series of 15 bicalutamide analogues (sulfide, deshydroxy, sulfone, and O-acetylated) were prepared and their antiproliferative activity evaluated against four different human prostate cancer cell lines (22Rv1, DU-145, LNCaP, and VCap). Bicalutamide and enzalutamide were used as positive controls. Seven of these compounds displayed remarkable enhancement in anticancer activity across the four PC cell lines. The deshydroxy analogue (16) was the most active compound with IC50 = 6.59-10.86 µM. Molecular modeling offers a plausible explanation of the higher activity of the sulfide analogues compared to their sulfone counterparts.
Keywords: androgen receptor (AR); bicalutamide; diarylpropionamide; prostate cancer (PC); sulfone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Pippione A.C., Boschi D., Pors K., Oliaro-Bosso S., Lolli M.L. Androgen-AR axis in primary and metastatic prostate cancer: Chasing steroidogenic enzymes for therapeutic intervention. J. Cancer Metastasis Treat. 2017;3:328. doi: 10.20517/2394-4722.2017.44. - DOI
-
- Jenster G., Van Der Korput H.A.G.M., Van Vroonhoven C., Van Der Kwast T.H., Trapman J., Brinkmann A.O. Domains of the human androgen receptor involved in steroid binding, transcriptional activation, and subcellular localization. Mol. Endocrinol. 1991;5:1396–1404. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-10-1396. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

