The Role of Probiotics in Cancer Prevention
- PMID: 33374549
- PMCID: PMC7793079
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13010020
The Role of Probiotics in Cancer Prevention
Abstract
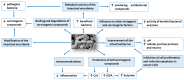
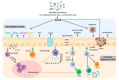
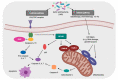
The gut microbiome can play important role in maintaining homeostasis in the human body. An imbalance in the gut microbiome can lead to pro-inflammatory immune responses and the initiation of disease processes, including cancer. The research results prove some strains of probiotics by modulating intestinal microbiota and immune response can be used for cancer prevention or/and as adjuvant treatment during anticancer chemotherapy. This review presents the latest advances in research into the effectiveness of probiotics in the prevention and treatment support of cancer. The described issues concern to the anticancer activity of probiotic microorganisms and their metabolites. In addition, we described the potential mechanisms of probiotic chemoprevention and the advisability of using probiotics.
Keywords: anticancer activity; gut microbiome; probiotics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Liśkiewicz P., Pełka-Wysiecka J., Wroński M., Bąba-Kubiś A., Samochowiec J. Intestinal flora and the pathophysiology of depression and anxiety disorders—Current state of the art and future perspectives. Psychiatry. 2018;15:70–76.
-
- Snyder L., Peter J.E., Henkin T.M., Champress W. Molecular Genetics of Bacteria. 4th ed. ASM Press; Washington, DC, USA: 1997. pp. 53–66.
-
- Joseph N., Vasodavan K., Saipudin N.A., Yusof B.N.M., Kumar S., Nordin S.A. Gut microbiota and short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) profiles of normal and overweight school children in Selangor after probiotics administration. J. Funct. Foods. 2009;57:103–111. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2019.03.042. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

