Biofilms as Promoters of Bacterial Antibiotic Resistance and Tolerance
- PMID: 33374551
- PMCID: PMC7822488
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics10010003
Biofilms as Promoters of Bacterial Antibiotic Resistance and Tolerance
Abstract
Multidrug resistant bacteria are a global threat for human and animal health. However, they are only part of the problem of antibiotic failure. Another bacterial strategy that contributes to their capacity to withstand antimicrobials is the formation of biofilms. Biofilms are associations of microorganisms embedded a self-produced extracellular matrix. They create particular environments that confer bacterial tolerance and resistance to antibiotics by different mechanisms that depend upon factors such as biofilm composition, architecture, the stage of biofilm development, and growth conditions. The biofilm structure hinders the penetration of antibiotics and may prevent the accumulation of bactericidal concentrations throughout the entire biofilm. In addition, gradients of dispersion of nutrients and oxygen within the biofilm generate different metabolic states of individual cells and favor the development of antibiotic tolerance and bacterial persistence. Furthermore, antimicrobial resistance may develop within biofilms through a variety of mechanisms. The expression of efflux pumps may be induced in various parts of the biofilm and the mutation frequency is induced, while the presence of extracellular DNA and the close contact between cells favor horizontal gene transfer. A deep understanding of the mechanisms by which biofilms cause tolerance/resistance to antibiotics helps to develop novel strategies to fight these infections.
Keywords: antibiotic resistance; antibiotic tolerance; biofilm control; biofilms; multidrug-resistant bacteria; recalcitrance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
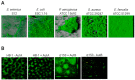
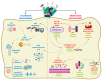
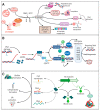
References
-
- O’Neill J. Tackling Drug-Resistant Infections Globally: Final Report and Recommendations; the Review on Antimicrobial Resistance. [(accessed on 5 August 2020)];2016 Available online: https://amr-review.org/sites/default/files/160525_Final%20paper_with%20c....
-
- WHO (World Health Organization) High Levels of Antibiotic Resistance Found Worldwide, New Data Shows. [(accessed on 8 August 2020)];2018 Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/detail/29-01-2018-high-levels-of-antibioti....
-
- EFSA (European Food Safety Authority) ECDC (European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control) The European Union summary report on antimicrobial resistance in zoonotic and indicator bacteria from humans, animals and food in 2017/2018. EFSA J. 2020;18:e06007. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2020.6007. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

