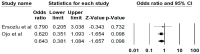Outcomes of Kidney Transplantation in Fabry Disease: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 33374610
- PMCID: PMC7838795
- DOI: 10.3390/diseases9010002
Outcomes of Kidney Transplantation in Fabry Disease: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Fabry disease (FD) is a rare X-linked lysosomal storage disorder with progressive systemic deposition of globotriaosylceramide, leading to life-threatening cardiac, central nervous system, and kidney disease. Current therapy involves symptomatic medical management, enzyme replacement therapy (ERT), dialysis, kidney transplantation, and, more recently, gene therapy. The aim of this systematic review was to assess outcomes of kidney transplantation among patients with FD.
Methods: A comprehensive literature review was conducted utilizing MEDLINE, EMBASE, and Cochrane Database, from inception through to 28 February 2020, to identify studies that evaluate outcomes of kidney transplantation including patient and allograft survival among kidney transplant patients with FD. Effect estimates from each study were extracted and combined using the random-effects generic inverse variance method of DerSimonian and Laird.
Results: In total, 11 studies, including 424 kidney transplant recipients with FD, were enrolled. The post-transplant median follow-up time ranged from 3 to 11.5 years. Overall, the pooled estimated rates of all-cause graft failure, graft failure before death, and allograft rejection were 32.5% (95%CI: 23.9%-42.5%), 14.5% (95%CI: 8.4%-23.7%), and 20.2% (95%CI: 15.4%-25.9%), respectively. In the sensitivity analysis, limited only to the recent studies (year 2001 or newer when ERT became available), the pooled estimated rates of all-cause graft failure, graft failure before death, and allograft rejection were 28.1% (95%CI: 20.5%-37.3%), 11.7% (95%CI: 8.4%-16.0%), and 20.2% (95%CI: 15.5%-26.0%), respectively. The pooled estimated rate of biopsy proven FD recurrence was 11.1% (95%CI: 3.6%-29.4%), respectively. There are no significant differences in the risks of all-cause graft failure (p = 0.10) or mortality (0.48) among recipients with vs. without FD.
Conclusions: Despite possible FD recurrence after transplantation of 11.1%, allograft and patient survival are comparable among kidney transplant recipients with vs. without FD.
Keywords: Fabry disease; kidney transplant; kidney transplantation; meta-analysis; systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Germain D.P., Oliveira J.P., Bichet D.G., Yoo H.W., Hopkin R.J., Lemay R., Politei J., Wanner C., Wilcox W.R., Warnock D.G. Use of a rare disease registry for establishing phenotypic classification of previously unassigned GLA variants: A consensus classification system by a multispecialty Fabry disease genotype-phenotype workgroup. J. Med. Genet. 2020;57:542–551. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2019-106467. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ashton-Prolla P., Tong B., Shabbeer J., Astrin K.H., Eng C.M., Desnick R.J. Fabry disease: Twenty-two novel mutations in the alpha-galactosidase A gene and genotype/phenotype correlations in severely and mildly affected hemizygotes and heterozygotes. J. Investig. Med. 2000;48:227–235. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources