Treatment of Men with Central Hypogonadism: Alternatives for Testosterone Replacement Therapy
- PMID: 33375030
- PMCID: PMC7792781
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22010021
Treatment of Men with Central Hypogonadism: Alternatives for Testosterone Replacement Therapy
Abstract
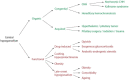
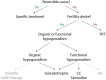
Central hypogonadism is a clinical condition, characterized by sexual symptoms and low serum testosterone levels, due to an impaired function of the hypothalamus or pituitary gland. Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) is the standard treatment for hypogonadism, but it has some disadvantages. TRT is not a good option in men wishing to preserve fertility, nor in men with (a high risk of) prostate cancer, polycythemia, thrombophilia and severe cardiovascular disease. In this review, we discuss alternative treatments for central hypogonadism. If reversible causes are present, non-pharmacological interventions can be therapeutic. Gonadotropins are a good alternative to TRT when fertility is desired in the near future though they require frequent injections. Clomiphene citrate and tamoxifen seem to be a safe alternative for the treatment of functional central hypogonadism in men, as several studies reported a significant increase in testosterone levels with these drugs. However, their use is off-label and data supporting the efficacy of clomiphene citrate and tamoxifen on hypogonadal symptoms are insufficient. For this reason, clomiphene citrate and tamoxifen should not be used in routine clinical practice to treat sexual symptoms in men with central hypogonadism.
Keywords: aromatase inhibitors; central hypogonadism; clomiphene citrate; functional hypogonadism; gonadotropins; hypogonadotropic hypogonadism; late-onset hypogonadism; tamoxifen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Corona G., Goulis D.G., Huhtaniemi I., Zitzmann M., Toppari J., Forti G., Vanderschueren D., Wu F.C., Corona G., Goulis D.G., et al. European Academy of Andrology (EAA) guidelines on investigation, treatment and monitoring of functional hypogonadism in males. Andrology. 2020:12770. doi: 10.1111/andr.12770. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bhasin S., Brito J.P., Cunningham G.R., Hayes F.J., Hodis H.N., Matsumoto A.M., Snyder P.J., Swerdloff R.S., Wu F.C., Yialamas M.A. Testosterone Therapy in Men with Hypogonadism: An Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018;103:1715–1744. doi: 10.1210/jc.2018-00229. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Boehm U., Bouloux P.M., Dattani M.T., de Roux N., Dodé C., Dunkel L., Dwyer A.A., Giacobini P., Hardelin J.P., Juul A., et al. Expert consensus document: European Consensus Statement on congenital hypogonadotropic hypogonadism-pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2015;11:547–564. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2015.112. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

